WAV Pros and Cons – WAV vs MP3
Pros
High-Quality Audio
The number
one reason that all professional sound engineers and producers use WAV files
over MP3 or any other file for that matter is its unbeatable audio quality.
Because the
WAV format is lossless it retains all quality and information from the original
recording.
Streaming services require WAV
Most distribution
agencies require WAV files for music distribution because of its excellent
quality.
For example, Amazon Music, Spotify, Apple Music, and many more, all require WAV files. They then convert to another format that is more suitable for streaming.
Cons
Large File Size
As we
mentioned earlier the file size can be quite large in comparison to MP3.
Although they can vary quite a lot depending on what sample rate and bit depth are used, a one-minute audio clip using the industry-standard sample rate and bit depth will be around 15mb.
Not easy to share
The sheer
size of WAVs files can sometimes make sharing these files quite difficult.
Sometimes a
song or project can contain 100+ different WAV files adding up to hundreds of megabytes
making it difficult to send projects to mixing or mastering engineers over the
internet.
Not good for portable devices
Some MP3
players can only play the MP3 format, but these devices have faded out and the
smartphone has taken over.
Smartphones have the capability to play many different formats but because WAV files are very large, only a small amount of data can be stored in comparison to MP3 or some other formats.
Below is an estimation of how many songs can fit on a 64GB device. MP3 vs WAV.
- MP3 – 8000 songs
- WAV – 800 songs
FLAC vs. WAV vs. MP3
Let’s get MP3s out of the way first, because they suck. If you have even a passing interest in audio fidelity and decent sound, you’re going to want to avoid these. Essentially, an MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3) is a file that sacrifices audio resolution for minimal size, cutting out all the bits that we as humans aren’t supposed to be able to hear, and can be read by just about any device on earth.
The downside? We might not technically be able to ‘hear’ the bits that are cut out, but in our opinion, this compression of the file – and we’re going to be using the terms compressed and uncompressed a lot – renders it thin, tinny, and lifeless. No one these days seriously uses MP3s – its creators recently terminated its licensing, declaring it dead. Regardless, you’ll still come across it every now and then, especially if you have an old iTunes Library.
FLAC is where things get really interesting. The Free Lossless Audio Codec pulls off a remarkable trick by allowing you to compress the file size down to roughyl 60% of the original, without losing any noticeable audio quality. Not only is it free and open source, but it allows the transmission of sample rates up to 1,411 kbps, which is significantly higher than anywhere else. This is the format of choice for the streaming service Tidal, and in terms of mass-market streaming audio, it’s considered the gold standard. This is the format you should use if you care deeply about your sound, but don’t want to commit to physical formats like CDs or vinyl.
WAVs are equally common, and useful for anybody wanting decent audio. Essentially, WAVs (Waveform Audio File Format) are higher resolution audio files, that almost always contain uncompressed audio. Technically speaking, a WAV file is simply a presentation of a piece of audio encoded with something known as Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). This is a way of taking analog audio and converting it into digital so that it has a sample rate and bit depth, as described above. Honestly? You don’t need to stress too much about the difference. For all intents and purposes, WAV and PCM are interchangeable terms, and both refer to a reasonably high-quality audio file. To make things even simpler: FLAC is commonly used on streaming services, whereas you’ll normally find WAVs and MP3s on a hard drive in your house.

Часть 4. FLAC или WAV: что лучше?
Теперь, когда вы получили всестороннее представление об этих форматах, таких как их качество, размер файла и т. д., какой файл вам следует выбрать? FLAC лучше WAV или наоборот? Если вам нравится качество вашего файла, выберите формат WAV и рассмотрите возможность хранения вашего устройства. Однако, если вы хотите создать доступную коллекцию песен, файл FLAC, безусловно, будет вашим партнером. Во-вторых, FLAC подходит для работы в Интернете, поскольку его легко хранить и загружать. Кстати, отправлять WAV-файл в Интернет довольно неудобно. WAV лучше, чем FLAC? Что ж, выбор за вами!
Key Differences Between WAV and MP3
- The audio encoding formats WAV and MP3 mainly differ by the extent of compression and quality. WAV preserves the quality of the audio file by employing negligible changes in the source file. As against, MP3 can produce the smallest size version of the same file in WAV format by removing similar data.
- By MP3 huge rates of compression can be achieved as compared to WAV.
- The size of the WAV file is generally higher than that of the MP3 file.
- MP3 format extremely degrades the audio quality while WAV file remains in good quality.
- WAV was developed by Microsoft and IBM. On the contrary, MP3 was devised by MPEG and which is a patented format.
WAV vs MP3
WAV is an uncompressed and lossless audio file format that is widely used for storing high-quality audio data. WAV files are capable of preserving the original audio quality. MP3 is a compressed and lossy audio file format that is widely used for storing and transmitting digital audio data.
The WAV file format is used when high-quality music is desired. In this file format, the audio files are not compressed.
Thus the quality of the audio files remains intact. As the files are not compressed, this file format takes up a lot of space for storing the audio file.
MP3 is the most common file format used for storing and transferring audio data. The format uses an algorithm to compress the audio files for storage.
As the audio is compressed, the quality of the file decreases. The audio further decreases with higher compression, and the file may sound distorted.
WMA: формат с небольшим размером файла, но потерями в качестве звука
WMA (Windows Media Audio) — это аудио формат, разработанный компанией Microsoft. Он широко используется для сжатия аудио файлов, таких как музыка и речь, с целью уменьшения размера файла и экономии памяти.
Одним из главных преимуществ формата WMA является его относительно небольшой размер файла. Это позволяет сохранять большое количество аудио материала на ограниченном объеме памяти, таком как жесткий диск или флеш-накопитель.
Однако, стоит отметить, что WMA является потерянным форматом сжатия звука, что означает, что он сжимает аудио данные путем удаления некоторой информации, которая может сказываться на качестве звука. Это отличает его от без потерь форматов сжатия, таких как FLAC или ALAC, которые сохраняют полную аудио информацию в исходном качестве.
Тем не менее, для многих пользователей WMA остается удобным форматом для хранения и передачи аудио файлов. Благодаря его небольшому размеру, WMA обеспечивает быструю передачу и загрузку файлов через сеть или Интернет, а также эффективное использование памяти на устройствах хранения данных.
В целом, хотя WMA обеспечивает небольшой размер файла, пользователи должны быть готовы к потерям в качестве звука по сравнению с без потерь форматами сжатия
При выборе аудио формата, важно учитывать свои потребности в качестве звука, доступность и совместимость с устройствами и программным обеспечением
The MP3 format.
MP3 has successfully carried out a revolution in the world of music. It’s the most popular and most common digital audio format. Although many think it’s quite modern, its roots go back to the 70s. Unlike WAV, MP3 is a compressed and lossy format. It means that converting any audio to MP3 will reduce its original quality and also reduce the size. The reduction in size and quality results from data being thrown away.
The advantages of MP3 are:
- MP3 files are of small size. They can be effortlessly distributed over the Internet, and big music libraries stored on computers or music clouds. That is the main reason why MP3 has become a standard for purchasing music.
- The overall sound quality is usually OK for most average listeners. Using poor headphones or built-in phone speakers, you’re likely to hear no difference at all.
- Converting WAV to MP3 is simple (but terrible).Taking this into account, it’s clear why MP3 is a great format for distributing, streaming and promoting music. However, this comes at some cost.Compressing a file causes quality loss. Compression can often result in strange audio artifacts that damage the audio quality, especially higher frequencies. MP3 is not suitable for mastering, mixing and recording. Lots of DJs use only the quality higher than 320 kbps to make sure all the tiniest sounds are clear to their listeners.
All you need is an audio player that can play most lossy and lossless formats, and this player is VOX Music Player for Mac & iPhoneThis player is a total game-changer in the world of audio players. Minimalistic design, easy-to-use interface, and a powerful sound engine provide the playback of the highest efficiency and quality. VOX supports most audio formats, from lossy (MP3, OFF, AAC, etc.) to Hi-Res aka lossless like WAV, FLAC, APE, ALAC lots of which aren’t supported by Apple’s native audio player. VOX is currently available for Mac & iPhone (and iPod). VOX for iPad currently being under development.

Key VOX features are:
- Lossy and lossless audio formats playback.
- Spotify and SoundCloud synchronization. Listen to all your playlist with one app.
- Mac & iPhone sync collections, so whatever you have, you have on both devices.
- Scrobbling to Last.fm.
- Customizable EQ with many presets.
- Access to more than 30,000 radio station.
TRY VOX MUSIC PLAYER FOR MACTo store your music, there’s a special locker called VOX Music Cloud Storage (formerly LOOP Unlimited Music Cloud Storage). VOX Cloud is an unlimited cloud available to VOX users exclusively which stores all your music regardless of the format, size or bit rate. It means that the cloud preserves the original sound and doesn’t compress or convert anything. In other words, you listen to what you upload.
Разница между WAV и MP3 для записи подкастов
Эмпирическое правило заключается в том, что вы всегда должны работать со звуком без потерь, например WAV. Вам нужно будет экспортировать только окончательную версию своего подкаста в MP3 для загрузки на хостинг.
Поскольку вы можете конвертировать WAV в MP3, но не наоборот (это возможно, но неразумно), сохраняйте все мастер-треки в WAV и публикуйте в MP3 только тогда, когда вы собираетесь доставить продукт или отправить его на предварительное прослушивание.
Работа с WAV при создании подкастов
Весь звук, записанный в таких программах, как Audacity или Adobe Audition, по умолчанию записывается в виде файлов WAV. Когда вы закончите запись, вы можете экспортировать ее в WAV, MP3 или другой аудиоформат. Мы рекомендуем вам экспортировать все ваши голосовые записи в WAV и просто добавить ключевое слово, например RAW, к имени файла. Например: «Подкаст «Краткая история Греции», часть 1, дубль 1 RAW.wav».
Таким образом, у вас всегда будет основная версия вашей записи, к которой вы всегда сможете вернуться, если в какой-то момент редактирование звука пойдет не так. После этого вам нужно будет поработать над улучшением закадрового голоса, например, применив шумоподавление, устранение щелчков и другие фильтры, и этот результат также можно экспортировать в формате WAV.
Когда использовать MP3 в конвейере создания подкастов
Если вы работаете над подкастами или создаете их, сохранение всех версий и шагов всех проектов в формате WAV без потерь может просто загромождать ваш диск и занимать свободное место. В этом случае вы можете экспортировать аудиофайлы в MP3, чтобы сравнить версии и поделиться ими с коллегами, которые смогут предварительно прослушать вашу работу. Не забудьте сохранить все свои мастер-треки в формате WAV на внешнем диске или в сетевом облаке, если у вас ограниченное пространство, например 128 ГБ.
Sample Rate And Bit Depth Explained
To understand how audio formats work, you need to understand two concepts: Sample Rate and Bit Depth. These are two measures that tell us how accurate a piece of digitally-recorded sound is, and we can understand them by imagining an art critic, looking at a painting. Yes, an art critic. Work with us here. Take a look at this wonderful piece of art:
 Boat and Yellow Hill – which we’ll use to explain sample rate and bit depth! | Ed Bierman
Boat and Yellow Hill – which we’ll use to explain sample rate and bit depth! | Ed Bierman
Let’s say this particular art critic really wants to get to grips with the painting above and really understand it, but can only look at it a certain number of times before she has to move on (she’s busy, OK?). Obviously, the more often the critic looks at the painting – the more she samples it – the more she’ll understand it. This art critic can look at the painting 44,100 times per second. Obviously, if her sample rate were higher – like 96,000 times a second – she’d understand more about the painting. (We’ll talk about why we picked those numbers below – for now, just roll with it).
Now let’s talk about the painting itself. Let’s say our super-speedy critic is looking at a small portion of the picture, which happens to be painted yellow. That’s a piece of information she now has. She also knows that there are many different shades of yellow, and will use that information to critique the painting. So, when she’s writing up her review, she’ll be able to describe that yellow section as butter yellow, or lemon yellow, or gold. Not just plain yellow.
Let’s also say she’s reasonably smart and has the ability to describe sixteen different shades of yellow. Each shade of yellow she can describe is a single bit of information – in this case, she has sixteen bits of information at her disposal. Couple that with her 44,100 glances at the painting, and she’ll have a very in-depth understanding of what she’s looking at.
(The analogy is a little crude, because computers work slightly differently, and sixteen bits of information actually refers to 2 to the 16th power which is 65,536 volumes and…look, trust us, you don’t need to know this, OK? Let’s just go with sixteen bits of information. Sixteen shades of yellow. Breathe, everybody. Breathe.)
Now think of this in music terms. A group of musicians in a studio is the painting, and the software recording them is the art critic. The software ‘looks’ at the incoming sound 44,100 times every second and is able to use up to 16 bits of information each time it does, in order to describe what it’s hearing. Audio recording on a regular CD or Spotify stream is 16-bit/44.1 kHz. Samples are always written as Hertz and kiloHertz (1,000 Hertz). You can record even higher-quality audio at 24-bit/192 kHz, which means that the software is sampling the music 192,000 times every second, and is able to draw on 24 bits of information to accurately describe it.
If none of the above is clear, then all you need to understand is this: the higher the bit depth and sample rate, the higher quality an audio file is.

MP3 & WAV differences
here are many differences between the MP3 and WAV audio formats, but the key difference is that MP3s are “compressed” and WAV files are – yes, that’s right – “uncompressed”.
That means that MP3s are smaller (around 1/10th of the file’s original size). So MP3s are easy to send around and they load quickly on a webpage, to name just two advantages. The disadvantage is that in the compression process they’ve lost 90% of the original audio! MP3s are considered a “lossy” audio file type.
WAV files are uncompressed. So the file contains all of the original elements. This means WAV files are “lossless” because you don’t lose any part of your audio when you create one. So WAV files are a more accurate audio clip and they provide objectively better quality. But, the downside is that they’re bigger, so they’re not as easy to work with, host, or distribute.
So size and quality are the main differences between WAV and MP3s.
What Is a WAV File
To eliminate the beeping noises commonly associated with computers, Microsoft and IBM introduced WAV files with their computer software. Those obnoxious sounds could be replaced with WAV files. WAV files are high-quality audio files that are simple to alter. That’s why professional music producers nowadays use WAV files with their audio editing software. . Keep in mind how WAV files are encoded when comparing the advantages and disadvantages of WAV vs MP3 files. This has an impact on their size and quality, which has an effect on how your program sounds and is distributed during playback.
Сравнение размеров аудио форматов: какой из них требует меньше памяти?
Размер аудио формата играет значительную роль при хранении и передаче аудио файлов. Чем меньше размер файла, тем меньше занимает памяти на устройстве, тем быстрее файл передается по сети и тем быстрее загружается на веб-странице.
Существует несколько популярных аудио форматов, каждый из которых имеет свои особенности и отличается по размеру:
MP3 — один из самых распространенных форматов, обеспечивает хорошее качество звука при сравнительно небольшом размере файла. Средний размер MP3 файла вполне может быть около 3-5 МБ в зависимости от битрейта — параметра, который определяет качество звука;
AAC — развитие формата MP3, обеспечивает лучшее качество звука при меньшем размере файла. Средний размер AAC файла обычно составляет около 1.5-3 МБ, что делает его более компактным по сравнению с MP3;
FLAC — формат без потерь, обеспечивающий максимальное качество звука. Файлы в формате FLAC занимают больше места, чем MP3 или AAC, и обычно составляют около 10-30 МБ
FLAC может быть полезен для аудиофилов и профессионалов, которым важно сохранить высокую точность звука;
WAV — формат без сжатия, сохраняющий абсолютно все данные звука. Файлы WAV занимают больше места на устройстве и в сети, и их размер обычно составляет около 30-50 МБ в зависимости от длительности записи;
OGG — формат с открытым исходным кодом, обеспечивающий хорошее качество звука и малый размер файла
Файлы OGG в среднем занимают около 2-4 МБ.
В итоге, выбор подходящего аудио формата будет зависеть от ваших потребностей и требований в отношении качества и размера файла
Если вам важно сохранить максимальную точность звука, FLAC или WAV могут быть лучшими вариантами. Если вы ищете хороший баланс между качеством и размером файла, MP3 или AAC подойдут лучше
Если же вы хотите минимизировать размер файла, OGG может быть предпочтительнее.
Необходимо помнить, что размер файла зависит не только от формата, но и от других факторов, таких как битрейт, длительность звука и специфика кодирования. Поэтому всегда рекомендуется проводить сравнение размеров различных аудио форматов на конкретных файлах и с учетом нужд конкретной ситуации.
MQA And Hi-Res Audio Explained
One of the things that streaming can’t do, and that actual files on a hard drive can, is deliver true high resolution audio. It’s a bit of a nebulous term, encompassing many things, but it essentially means audio of the very highest quality. We are a tad dubious about manufacturers trumpeting their products as handling it, mostly because it’s so ill-defined, but it’s out there. And there’s been a development recently that might bring it to streaming services.
It’s called MQA (Master Quality Authenticated). Essentially, it delivers tiny files with absolutely enormous sound quality, using some sophisticated digital jiggery-pokery to package them into a FLAC or WAV container, and deliver them down your piddly Wi-Fi signal.
On the one hand, this is obviously great news for audiophiles and their files… On the other, it hasn’t quite taken the industry by storm. MQA is still readily available, but it has yet to make a real dent into the dominant file formats of our time. Although for the record, we would love to see it do so. You can actually listen to MQA audio on Tidal right now, thanks to their Tidal Masters lineup on desktop. You also need compatible hardware to actually run it – like DSD, it requires some fairly specialized internal components to get it working. Fortunately, these things are becoming more readily available. Products like the Mytek Brooklyn Bridge will quite happily handle MQA sound.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is WAV the best audio format?
WAV is one of the highest-quality, lossless audio formats suitable for professional applications where sound quality is given the most priority. However, we cannot call it the best audio format because there are some downsides, like limited compatibility and larger file size.
2. Does WAV to MP3 reduce quality?
Yes, converting a WAV file to MP3 will significantly lose audio quality as the soundtrack will undergo compression and lose some of the original data.
3. Should I use WAV or MP3 for video?
MP3 is the preferred format in most video applications because it is much smaller in size, has better compatibility options, and is easier to use. WAV is only suitable for high-end, professional video production where both audio and video quality are critical.
A Brief History of the MP3
Karlheinz Brandenburg, a professor at the Fraunhofer Institute was one of the lead developers of the MP3.
He was also one of the first people to push for the use of psychoacoustics.
By the late 1980s, the MP3 was almost ready but still having issues dealing with the human voice.
The song Tom’s Diner by Suzanne Vega is a common choice amongst audiophiles for testing sound systems.
The A Capella version of Tom’s Diner would also be the first track chosen to test the MP3.
Initially, MP3 compression absolutely destroyed the track leading to hundreds of revisions to get it right.
Ghost in the MP3 is a project by Ryan Mcguire who created a track from the discarded/leftover sounds from Tom’s Diner after compression.
The MP3 format still widely divides opinion but whether you think it saved the industry or ruined it, it certainly had a huge effect on it.
There were some seminal moments in the history of MP3: the release of the Winamp media player for Windows in 1997 was huge.
In the late 1990’s I think everyone with a PC created Winamp playlists full of MP3s.
The big change was that people could now have hundreds of songs on their computer without filling up their entire hard drive.
Furthermore, people could easily share these songs with others.
This development gave birth to a host of illegal file-sharing platforms.
In 1999 came Napster, the most infamous of the peer2peer sharing platforms which would be caught up in endless legal battles with most of the record industry.
The next huge development was making this music portable.
The very first MP3 player was the MPman, released in 1998, and then Apple soon joined the market in 2001 with iTunes and the iPod.
As we all know, the iPod in its various forms took the world by storm and the MP3 along with it.
When you purchase music from iTunes it’s in the AAC format but you can still convert to MP3 to transfer to compatible devices.
MP3 players have of course been all but forgotten.
Most mobile phones now have enough storage for all the music you can handle. Because of this, MP3s are actually a daily feature in many people’s lives.
В MP3 умещается все: цифра
Строго говоря, с большинством цифровых записей — та же самая картина. В 90-е годы и позднее появились дешёвые пластмассовые бумбоксы. Звукорежиссёрам пришлось заботиться о едином звучании на всех устройствах — динамический диапазон записей порезали до 10-12 бит.
Еще один момент. До недавнего времени никто не записывался на студии слишком в высоком качестве. Потому что одновременно работать с несколькими десятками аудиодорожек с высоким качеством записи сложно, а иногда просто недостаточно человеческих и технических ресурсов.
Если все это кажется неубедительным — посмотрите результаты любого слепого теста. Можно распознать систему, можно распознать наушники. Но вот отличить качественный MP3 (CBR 320 kbps, Lame 3.93) от FLAC удается только самым прокаченным гурманам.
Хочешь ещё?
Ищешь ответ на вопрос?
iPhones.ru
Консерваторию не заканчивали? Тогда losseless Вам не нужен, слушайте качественный mp3. Очень часто встречаются индивиды, презирающие сжатые форматы в принципе. Не стоит ориентироваться на их мнение. Очередные модники, которые в исследовании с вероятностью 90% не услышат отличий сжатого звука от несжатого. Что такое mp3 MP3 придуман не только для того, чтобы резать качество. Его разработкой…
What is a WAV File?
A WAV file is a raw audio format created by Microsoft and IBM. This format uses containers to store audio data, sample rates, and bitrates.
They work by taking an audio signal and converting it to binary data.
An analog to digital converter takes thousands of snapshots per second to capture the full audible frequency range of 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
WAV files are lossless and uncompressed which means they lose no quality from the original recording.
WAV files are large and take a lot of space.
A stereo, CD-quality recording (44.1 kHz, 16 bit) averages around 10 MB per minute.
Increasing to 48 KHz and 24 bit stereo will be reflected in a change from 10 Mb per minute to 16.48 Mb.
An average three-minute song would require approx. 33Mb of disk space.
That was an overview of what MP3 and WAV files are.
We can now take a closer look at some of the differences between the two.
The biggest difference is that MP3s are compressed audio and WAV files are uncompressed audio.
Compression, in this context, is the process of reducing the size of an audio file.
Визуальное сравнение WAV и MP3
Для визуального сравнения двух форматов и их характеристик мы воспользуемся бесплатным инструментом Audacity с установленным кодеком LAME MP3 Export Library (версия 3.1). Мы запишем закадровый голос и сохраним файл сначала в формате WAV, а затем в формате MP3.
Графический снимок WAV
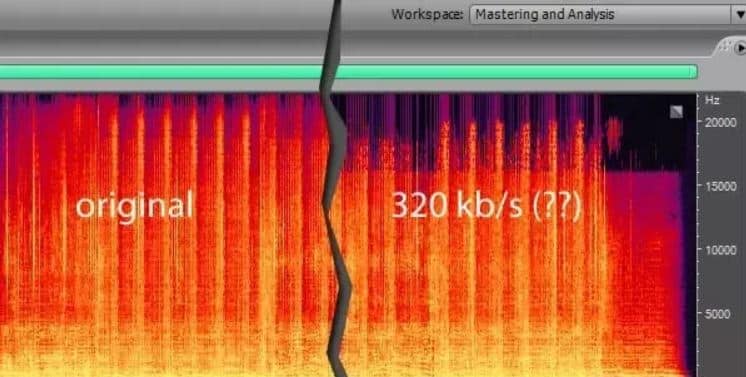
Вот изображение файла WAV в двух представлениях: просмотр формы сигнала и просмотр спектрального анализа, который дает больше информации об объеме данных на частоту. Как мы видим, данными заполнен весь спектр от 0 Гц до 22 000 Гц.
Как читать спектральный анализ
Представление спектрального анализа может быть трудным для чтения, если вы видите его в первый раз. Он используется для ссылки и редактирования ваших записей в профессиональных приложениях, таких как iZotope RX, но в Audacity также есть такое представление.
На этой диаграмме вы можете увидеть интенсивные базовые низкие частоты мужского голоса (от 80 до 160 Гц) в нижней части белого цвета. По большей части это гласные звуки. Красные шипы — это слоги (например, S). Естественный шум имеет синий цвет на более высоких частотах и выглядит точно так же, как белый шум по телевизору.
Графический снимок в формате MP3
Как видите, всех частот выше 20 000 Гц не существует, поскольку они были вырезаны при сжатии. В сжатии MP3 есть гораздо больше, чем эта операция, но эта самая очевидная. Если мы увеличим масштаб, мы увидим больше различий в спектральном представлении между WAV и MP3, однако большинство этих различий не влияют на качество звука.
Encoding MP3 Files
The way WAV and MP3 files are encoded is one of the most significant differences. MP3 files are compressed to make them smaller and easier to manage. Consequently, they have a lower audio quality and are referred to as “lossy” audio files. To reduce the file, some sections of the MP3 audio are removed during the encoding process (to make it smaller). Perceptual coding, also known as psychoacoustic modeling, is a method of changing audio signals that results in the loss of some sound that is deemed beyond the hearing capabilities of most people.Keep in mind that although the procedure has an impact on audio quality, you’re unlikely to notice a difference between MP3 and WAV quality. If you utilize MP3 or WAV files, your listeners are unlikely to notice, especially if your podcast includes speech (and less music).
Что такое файл MP3?
Это цифровой формат для шифрования аудио данных, который основан на другом формате — MPEG2. Отсюда и получил расширение с тройкой на конце.
Первый патент на этот формат был зарегистрирован в Германии в апреле 1989 года. Патент был зарегистрирован на немецкое исследовательское общество Фраунгофера. Отцом формата является Карлхайнц Бранденбург (Karlheinz Brandenburg). Самая первая песня, на которой тестировался этот формат — «Tom’s Diner» певицы Сюзанны Вега.
Первый официальный файл появился в 1995 году.
Этот формат довольно быстро стал отраслевым стандартом для записи аудио файлов.
Файлы MP3 до сих пор широко используются из-за удобства работы с ними и их меньшего размера. В 2017 году правообладатель формата, общество Фраунгофера, официально заявило об окончании поддержки этого формата.
Карлхайнц Бранденбург отец формата MP3