Simple Past/Present Perfect Simple – Free Exercise
Lingolia Plus English
Unlock all grammar exercises for English with a Lingolia Plus account
- 1037 interactive grammar exercises for English
- sorted by topic and level (A1–C1)
- with a built-in progress tracker and awards system
Simple Past/Present Perfect Simple – Lingolia Plus Exercises
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: comparison 1B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: comparison 2B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: comparison 3B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: comparison 4B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: comparison 5B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: comparison 6B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: comparison 7B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple (1)B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple (2)B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple (3)B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple (4)B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple (5)B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple (6)B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple (7)B2
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple (8)B2
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: questionsB1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: recent or further back?B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: finished vs. unfinished time periods (1)B1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: finished vs. unfinished time periods (2)B2
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: mini dialoguesB1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: Malala YousafzaiB1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: dialogueB1
Simple Past – Present Perfect Simple: Phiona MutesiB2
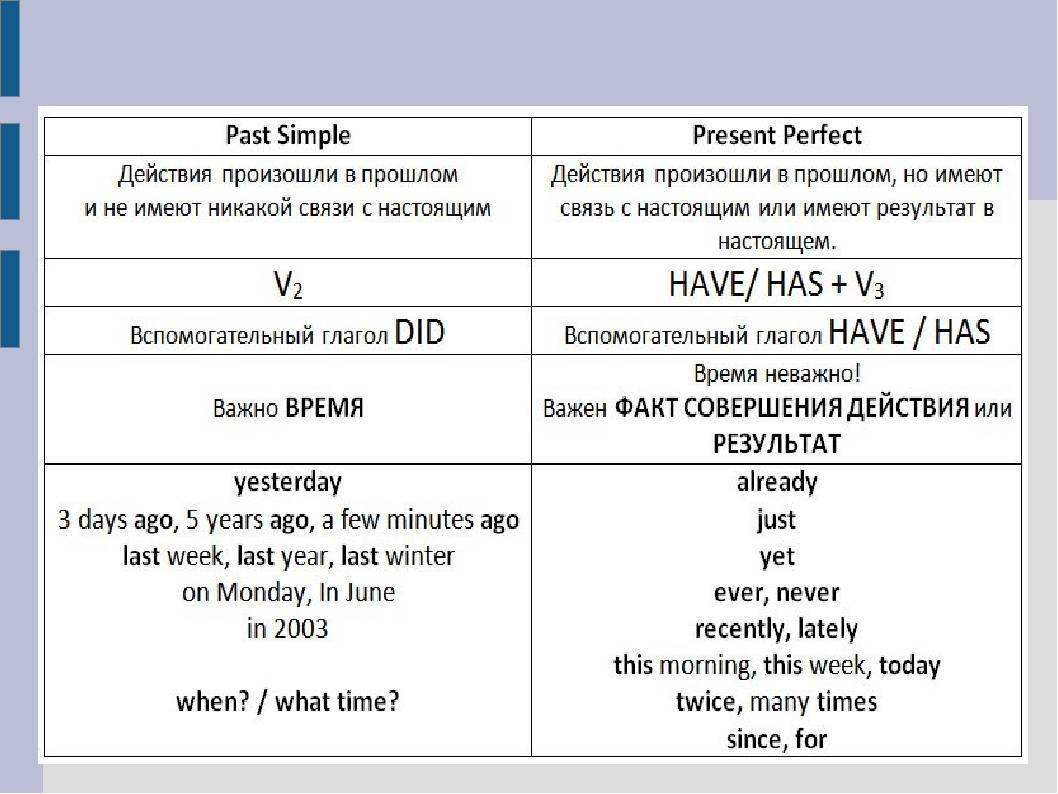
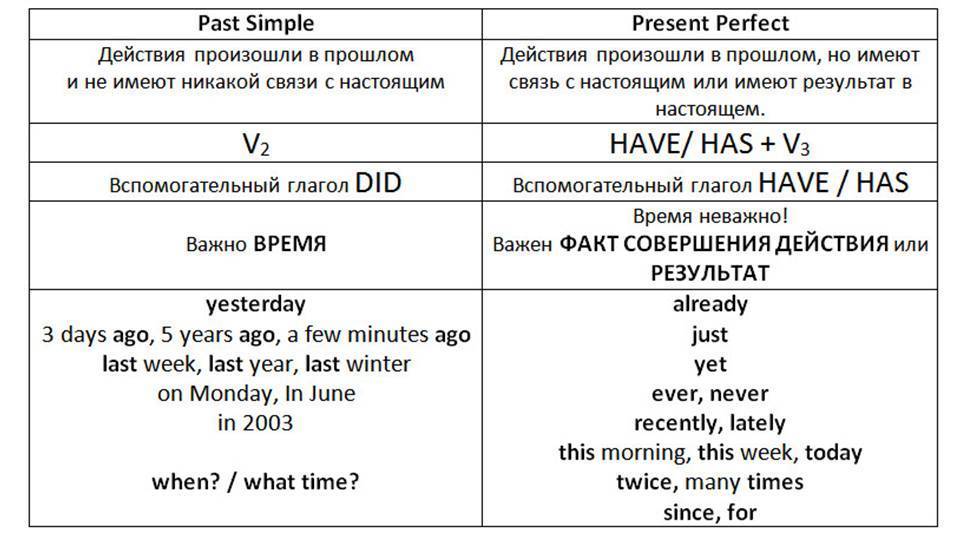
Past Simple — действия, события или состояния, случившихся в прошлом и законченных в прошлом
Past Simple применяется в разговоре об обычных ситуациях или исторических фактах.
Примеры:
I went to the shop and bought “Star Wars” cassette. — Я пошёл в магазин и купил кассету со «Звёздными войнами».
My father saw «Star Wars» in 1977. He is a real fan! — Мой отец посмотрел «Звёздные войны» в 1977 году. Он — настоящий фанат!
Смысл этих предложений — озвучить какой-то факт, который не влияет на контекст в настоящем, будущем или прошлом. Мой отец просто посмотрел фильм в 1997. Я просто сходил и купил кассету.
Понять, что нужно употребить Past Simple, часто помогают слова, указывающие на конкретный момент времени в прошлом:
- yesterday — вчера;
- last year/week/month/century — в прошлом году/на прошлой неделе/в прошлом веке;
- a long time ago — давно;
- two days/three weeks/several years ago — два дня/три недели/несколько лет назад;
- in 1977 — в 1977 году.
Когда слов-маркеров в предложении нет, стоит обратить внимание на контекст. Past Simple используется, если:
- В предложении непоколебимо отрицается какой-либо факт.
I never lied about my love to “Star Wars”. — Я никогда не лгал о своей любви к «Звёздным войнам».
- Речь идёт о прошлых привычках человека.
She always watched “Star Wars” on Sundays with her little brother. — Она всегда смотрела «Звёздные войны» по воскресеньям со своим младшим братом.
- Речь идёт о только что случившемся событии.
Mark purchased the new version of “Star Wars” game for his PlayStation. — Марк купил новую версию игры «Звёздные войны» для своей приставки (секунду назад).
- Вы описываете внешность или состояние человека, а также погодные условия.
They looked happy while watching “Star Wars”. — Они выглядели счастливыми, пока смотрели «Звёздные войны».
It was sunny outside, but they decided to stay at home and continue watching. — Снаружи было солнечно, но они решили остаться дома и продолжить просмотр.
- Нужно перечислить какие-то события в прошлом.
We watched “Star Wars”, ordered pizza and fell asleep. — Мы посмотрели «Звёздные Войны», заказали пиццу и уснули.
Когда вместо Present Perfect используется Past Simple
Как видно из примеров выше, грамматическая конструкция Present Perfect длиннее и сложнее, чем в Past Simple. В разговорной речи носители языка и жители англоязычных стран привыкли упрощать и сокращать формулировки. Именно поэтому не стоит удивляться и спешить исправить человека, если в ситуации, когда, очевидно, нужно использовать настоящее совершенное время, он вдруг формулирует мысль в простом прошедшем.
Правильно: I have drank too much, I can’t remember even the main heroes’ names in “Star Wars” — Я выпил слишком много, что даже не могу вспомнить имена главных героев «Звёздных войн».
Говорят: I drank too much, I can’t remember even the main heroes’ names in “Star Wars” — Я выпил слишком много, что даже не могу вспомнить имена главных героев «Звёздных войн».
В описанной ситуации действие «выпил» как факт употребления алкоголя и «выпил» как описание ситуации, в которой человек чувствует себя немного расфокусированным, даже в русском языке выражается одинаково.
Отрывок из Курса “английский для Среднего уровня” – Объяснение Present Perfect с примерами и тренировкой
Формула Present Perfect проста:
have/has + глагол действия с окончанием -ed (для правильных глаголов) или третья форма глагола (для неправильных).
Правильно, не забываем, что есть правильные и неправильные глаголы.
Для Present Perfect нам нужна третья форма. Возьмем снова глагол fly — здесь используем форму flown.
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| A bird has just flown over you. | Над вами только что пролетела птица. |
| I have (I’ve) bought him a present already. | Я уже купила ему подарок. |
| I’ve been there already. | Я уже был там. |
| I’ve met you. | Я встретил тебя. |
| I’ve checked it on Google. | Я проверил это в Google. |
И да, в отрицаниях и вопросах, в отличие от Past Simple, глаголы остаются в третьей форме. В вопросах перед подлежащим мы ставим have/has – используем его каждый раз, когда делаем вопрос.
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| Has she finished that picture already? — No, she hasn’t. | Она уже закончила эту картину? — Нет, не закончила. |
| Have you ever seen the Milky Way? — Yes, I have. | Вы когда-нибудь видели Млечный путь? — Да, я видел. |
В отрицаниях добавляем “not” к have/has — have not/haven’t, has not/hasn’t.
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| I have not seen them yet, but I have called John. | Я их еще не видел, но я позвонил Джону. |
| She hasn’t walked her dog yet. | Она еще не выгуливала свою собаку. |
| They haven’t watered our flowers. The soil is dry. | Они не поливали наши цветы. Почва сухая. |
Past Perfect
Какое-то действие закончилось к определенному моменту в прошлом и вам важно это подчеркнуть в предложении?
Past Perfect вам в помощь!
Именно он обозначает прошедшее завершенное время.
Наши заветные маркеры: before (до), by that time (к тому времени), hardly … when … (едва…, как…), no sooner … than …. (едва… как …).
Чтобы добиться нужного эффекта, соедините вспомогательный глагол have в прошедшем времени с нужной формой глагола действия: had + глагол, выражающий действие, в третьей форме, либо с окончанием -ed (если глагол правильный).
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| They had moved to London before Jeremy was born. | Они переехали в Лондон еще до рождения Джереми. |
| I had graduated from the university by the time I married her. | К тому времени, когда я женился на ней, я уже окончил университет. |
| Google had been invented long before you were born! | Google был изобретен задолго до вашего рождения! |
Чтобы задать вопрос, поставьте вспомогательный глагол Past Perfect — had — перед подлежащим.
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| Had you consulted a doctor before you bought that medicine? | Консультировались ли вы с врачом, прежде чем купить это лекарство? |
| Had she found her dog before she left? | Нашла ли она свою собаку перед отъездом? |
С отрицанием обычная схема: had not/hadn’t
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| They hadn’t bought the snacks before the party last Friday. | Они не купили закуски перед вечеринкой в прошлую пятницу. |
| She hadn’t finished the project before her trip to France last year. | Она не закончила проект до своей поездки во Францию в прошлом году. |
Future Perfect
Это будущее совершенное время. Используем Future Perfect, когда нам нужно отметить, что действие завершится к какому-то моменту.
Маркеры для него будут примерно такими же, хоть речь и идет о будущем.
Will + have + нужная форма глагола, выражающего действие (используем третью форму у неправильных глаголов, либо добавляем окончание -ed) — и время готово.
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| I will have learnt all the English tenses by my next journey to Melbourne. | К моей следующей поездке в Мельбурн я выучу все английские времена. |
| They will have sold this dress by the end of summer. | Они продадут это платье к концу лета. |
| I will have found the dog by the time its owner returns. | Я найду собаку к тому времени, когда вернется ее владелец. |
| I’ll have finished the book by next winter. | Я закончу книгу к следующей зиме. |
В вопросе просто поставьте will перед подлежащим.
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| Will you have bought a car before we start our trip? | Купите ли вы машину до того, как мы начнем наше путешествие? |
| Will I have married Rob before he goes abroad? | Выйду ли я замуж за Роба до того, как он уедет за границу? |
Чтобы сделать отрицательное предложение, добавьте not к will.
| Пример на английском | Перевод на русский |
|---|---|
| I will not have practiced this trick long enough before the show starts. | Я не буду практиковать этот трюк достаточно долго до начала шоу. |
| They will not have finished their journey before next autumn. | Они закончат свое путешествие не раньше следующей осени. |
Согласитесь, полезные материалы!
What is the difference between Simple Past and Present Perfect Tense?
Perfects indeed are pesky, as the title says. OK, the University of California Department of Linguistics says the same thing to be honest. Whereas some tenses are easier to learn than others, as is to be expected, Perfects are usually what causes a headache to many an English learner.
Most of the time, using perfective tenses boils down to developing that fabled “feeling” for the language, i.e. knowing what to use and how to use it without knowing why. Sounds a bit out there, right?
But it really isn’t, as the more time you spend learning a language, the better you get to know it, the easier it becomes to just use it correctly, without burdening yourself with the grammar of it all. But, before that time, we’re going to help you differentiate between the to in as much detail as we can.
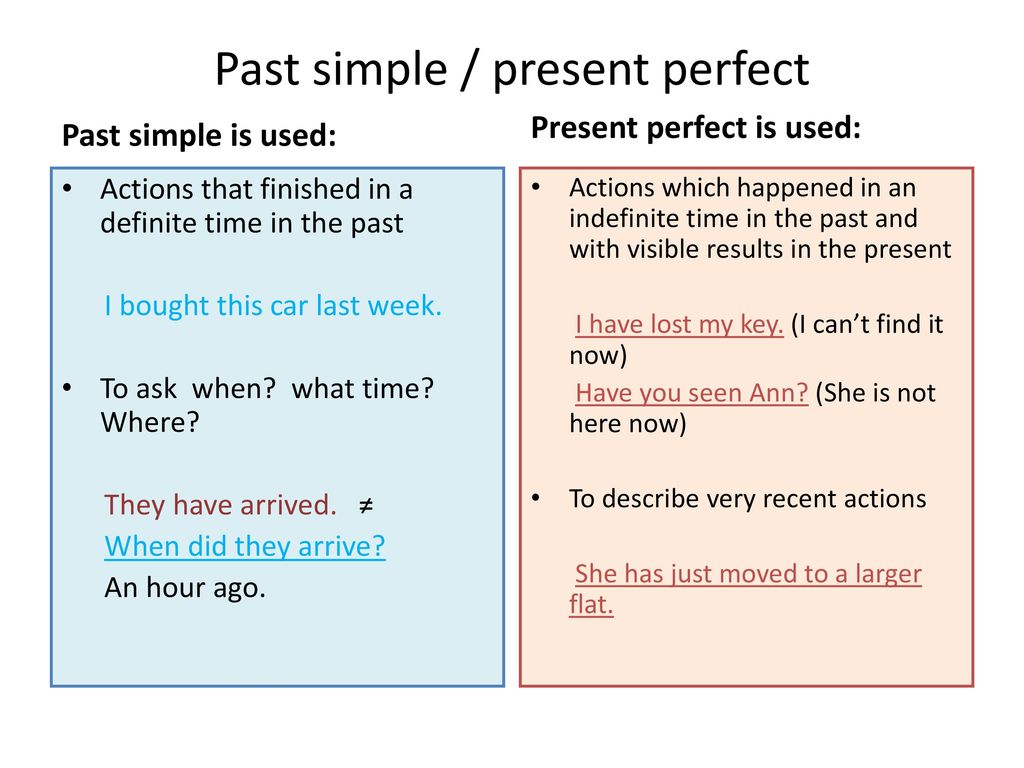
When do I use Past Simple Tense?
In order to know when to use Present Perfect, and when to use Past Simple, you first have to know when to use one, and when the other. So, you use Past Simple Tense for actions that started in the past, happened in the past, and finished in the past. That’s it.
You would usually know when such an action occurred, or it would be logical from your statement that the action is done for. For example: “I bought a new sweater yesterday.” or “My friend gave me a beautiful birthday present.”
When do I use Present Perfect Tense?
When it comes to Present Perfect, you can use it on a bunch of occasions:
- Continuing action – If an action started in the past, but continues still, it’s Present Perfect time! “I have lived in this town for seven years.”
- Unfinished time period – If an action happened during a period of time that still lasts, you use Present Perfect. “I’ve been to the cinema three times this week.” What a cinephile!
- Recent events – If something’s just happened, you use “just”, and Present Perfect, same as us. “She has just finished eating breakfast.”
- Time not important – If it’s not important to say when exactly an event took place, you use Present Perfect. “Yes, I have read ‘Crime and Punishment’.”
- Life experience – If you’re going to comment on the stuff you did or didn’t do in your life, feel free to use Present Perfect. “I have never been to Australia.” or “I’ve tried paella and it’s incredible!”
What is the difference, then?
We’ve presented you with many options describing when to use Present Perfect Tense, as we think it’s important for you to know. However, it can be confusing, so it’s best to use this simple rule of thumb – If you know when an action happened in the past, use Past Simple. If you don’t, or it’s not important, use Present Perfect. It’s easy when put like this?
Бонус для продвинутых
Today I’ve got up. I’ve brushed my teeth. I’ve drunk a cup of coffee. Вроде бы с тем, что произошло сегодня, мы используем Present Perfect. Но выглядит это сложновато, согласитесь? Выдыхаем, перечислять события можно в Past Simple. Даже если это today или this month. Поэтому правильно будет так: «Today I got up, brushed my teeth and drank a cup of coffee».
Чтобы точно понять разницу между Past Simple и Present Perfect, посмотрите видео от нашего америкашки Дэни. Он разбирает четыре случая, когда точно нужен Present Perfect.
Все мои заметки — в курсе «Как перестать путать английские времена».
How you doin’? Второе различие Past Simple и Present Perfect
Мы сказали, что если указано время, то мы используем Past Simple
НО! Обрати внимание: это должен быть законченный период времени
Давай посмотрим на примерах. 1 сезон 4 серия. Рэйчел, Моника и Фиби вспоминают о своих прошлых проступках. Моника припоминает Рэйчел 7-й класс:
Monica: Well, at least ‘big girls’ don’t pee in their pants in seventh grade! (Ну, по крайней мере ‘большие девочки’ не писаются в штаны в 7-мом классе!) Rachel: I was laughing! You made me laugh! (Я смеялась! Ты меня рассмешила!)
Девушки говорят о давно прошедшем периоде жизни: 7-й класс. Использован Past Simple.
Present Perfect же используется, если время еще не закончилось: this week / month/ year, two months / years, since Monday / 2000 / 5 a.m. Также со словами вроде: ever, never, in my life, имея в виду, что жизнь – это тоже отрезок времени, который не закончился.
Самая первая серия. Рэйчел сбежала от жениха и радуется началу новой, самостоятельной жизни, показателем которой, как ей кажется, является то, что она сама сварила кофе:
Rachel: Isn’t this amazing? I mean, I have never made coffee before in my entire life. (Разве это не удивительно? То есть, я никогда в жизни не делала кофе).
Запомни эти маркеры для Present Perfect: just, already, yet, ever, never, this week / month / year, two months / years, since Monday / 2000 / 5 a.m. и т.д.
РЕЗЮМИРУЕМ:
| Past Simple | Present Perfect |
| Для выражения прошедшего действия, если период времени уже закончился: yesterday, last week, on Sunday, an hour ago, long ago, the other day, in 1990. | Для выражения законченного действия, если период времени, в который это действие совершилось, еще не закончился: today, this week, ever, never и т.д. |
How do you use Present Perfect and Past Perfect?
We’ve already explained, and in great depth if we may add, all the possible uses of Present Perfect Tense. So no need to repeat ourselves. However, Past Perfect Tense is still somewhat of a mystery, isn’t it?
Let’s focus on it for a second? There’s really only a single reason to use Past Perfect, and it’s to describe an action that happened in the past, but before another past action or before a certain point in time.
Look at Past Perfect as that tense that tells about the days of yore, that describes events from the incredibly distant past, or an event that happened before another one. For example, “He had forgotten to bring his keys when he left the house.” OK, this one’s not so distant after all.
How do I differentiate between Past Perfect and Present Perfect?
This one sounds difficult, but it actually isn’t. In fact, it’s much more difficult to learn when to use Past Simple, and when Present Perfect. And you’ve already learned that, so this should be a walk in the park.
And that’s just what it is. Listen – it’s time for that rule of thumb again. Only use Past Perfect when talking about the past, a distant past, where one even happened before another one. Use Past Perfect for the event that happened first (or last? what?), and you’re good to go. Don’t even throw Present Perfect into the mix on this one!
We Were On a Break! Первое отличие Present Perfect от Past Simple
Past Simple используется для выражения законченного прошедшего действия, когда указано конкретное время, например: yesterday, last week, on Sunday, an hour ago, long ago, the other day, in 1990.
1 сезон 7 серия. Чендлер застрял в вестибюле банкомата с моделью Джилл Гудакр. В телефонном разговоре Джилл говорит своей маме, что застряла с «каким-то парнем», и Чендлер начинает фантазировать и говорить «про себя»:
Chandler: Oh! Some guy. Some guy. ‘Hey Jill, I saw you with some guy last night. (О, какой-то парень. Какой-то парень. ‘Эй, Джилл, я видел(а) тебя с каким-то парнем прошлым вечером’).
Чендлер представляет, как Джилл говорят, что видели ее с каким-то парнем прошлым вечером. Названо точное время – использовано время Past Simple.
Теперь найдем этот же глагол, но в Present Perfect. Перемахнем в 10-й сезон, 7-ю серию и вновь возьмем реплику Чендлера. В их с Моникой квартире раздается звонок, Чендлер берет трубку и затем спрашивает у Моники, не видела ли она биту Джо:
Chandler: Have you seen Joey’s bat? (Ты не видела биту Джо?)
На этот раз не указано времени, да оно и не важно – главное результат: видела ли Моника биту, а следовательно, знает ли она, где находится искомый предмет
РЕЗЮМИРУЕМ:
Past Simple
Present Perfect
Для выражения законченного прошедшего действия, если время указано.
Для выражения законченного действия, если время не указано, оно размыто
Время не важно – важен результат.
Употребление Past Simple
Простое прошедшее время употребляется как раз для тех случаев, когда нужно показать факт совершения действия в прошлом и дать понять, что эта ситуация не имеет никакой связи с настоящим, она закончилась где-то раньше. Типичные указатели на Past Simple – это слова yesterday, ago, last, previous, etc., а также точные даты и годы в прошлом:
· I met Tom at the station last Sunday – Я встретил Тома на вокзале в прошлое воскресенье · Did you watch that wonderful match yesterday? – Ты смотрел вчера тот замечательный матч? · Last time I tried to call him a week ago, but he didn’t answer – В последний раз я пытался позвонить ему неделю назад, но он не ответил
Есть один случай употребления, где мы используем только Past Simple, а не Present Perfect. Речь идет о специальном вопросе, начинающемся со слова when. Такие предложения в прошедшем времени выглядят более логично, чем в настоящем совершенном, ведь, задавая вопрос с when, говорящий спрашивает о времени или дате в прошлом, а такая ситуация не может иметь отражения в перфекте:
· When did you buy this nice carpet? – Когда ты купила этот красивый ковер? · When did he visit her granny last time? – Когда он навещал свою бабушку в последний раз?
The Past Simple
What Is It?
The past simple (also called the simple past) is the tense we use to talk about any action or event that has already happened.
When Do We Use It?
We use this tense when we know the exact or specific details of the time of the event (such as yesterday, the previous winter, last year, five hours ago and so on). In other words, the event is already over and finished.
Here are some examples:
We may also use this tense when we want to focus on telling people about the action.
Here are two examples:
In both cases, the focus is on telling of the action (“dancing a lot,” “walking home”) that took place in the past and not on the results or consequences of the action. We’re just talking about an event in the past and aren’t discussing the possible effects of it.
To sum up, we use the simple past to refer to an event or an action that took place in “finished time” or to simply focus on talking about the action itself.
Verb Forms to Use with the Past Simple
To write a sentence in the simple past, we have to convert the verb to its simple past form.
But verb conjugation can be tricky to get a hang of.
For regular verbs, there are a few rules regarding how to convert them. But for irregular verbs, you need to memorize the verb forms.
Let’s take a regular verb like to walk and an irregular verb like to eat, for example.
She walked home from the party.
(We added an “-ed” to “walk”)
He ate a pizza for dinner.
(“Eat” changes to “ate”)
If you’re feeling intimidated or confused about verb conjugations, don’t worry! All it takes is a bit of practice and soon it’ll become second nature. Here are some more example of past simple conjugations:
To cook — cooked
To study — studied
To play — played
To break — broke
To catch — caught
Употребление времени Present Perfect
Использование Present Perfect позволяет более точно выразить связь между прошлыми и настоящими событиями
Оно подчеркивает результаты и последствия действий, а также акцентирует внимание на актуальности этих событий
Например: «I have lived in this city for 10 years» (Я живу в этом городе уже 10 лет). В данном случае акцент делается не на конкретные годы проживания, а на факт того, что я все еще живу здесь.
Другие примеры использования Present Perfect:
- I have already finished my homework. — Я уже закончил свою домашнюю работу.
- Has she ever been to Paris? — Она когда-нибудь была в Париже?
- We haven’t seen each other for a long time. — Мы не видели друг друга давно.
- Have you ever tried sushi? — Ты когда-нибудь пробовал суши?
В этих предложениях Present Perfect используется для выражения действий, которые произошли в прошлом (закончил домашнюю работу, была в Париже), но имеют отношение к настоящему моменту (уже закончил, когда-нибудь была). Кроме того, указатели времени «already» и «ever» помогают указать наличие или отсутствие опыта или выполнения действий.
Правила образования Present Perfect
Основные правила образования Present Perfect следующие:
- Глагол в форме Present Perfect образуется с помощью вспомогательного глагола have (has для 3-го лица единственного числа) и основного глагола в третьей форме. Например: They have traveled to many countries. (Они побывали во многих странах.) She has visited her grandparents. (Она навещала своих бабушку и дедушку.)
- При отрицательной форме добавляется отрицательная частица not после вспомогательного глагола «have». Например: They haven’t finished their homework yet. (Они ещё не закончили свою домашнюю работу.)
- Конструкция Present Perfect часто используется с предлогами for (в течение) и since (с).
Примеры предложений с использованием Present Perfect:
- Have you ever been to Paris? (Ты когда-нибудь был в Париже?)
- She has lost her keys again! (Она опять потеряла свои ключи!)
- We have seen that movie before. (Мы уже видели этот фильм.)
Построение предложений Present Perfect
Построение предложений с использованием Present Perfect является одним из важных аспектов грамматики английского языка. Отличительной особенностью данного времени является его связь с настоящим моментом времени. Давайте рассмотрим правила построения предложений в Present Perfect и приведем несколько примеров.
Построение предложения: — Субъект + have/has + глагол в третьей форме (V3) + дополнение.
Примеры:
- Я уже позавтракал. (I have already had breakfast.)
- Они еще не закончили работу. (They haven’t finished the work yet.)
- Она уже посетила эту страну дважды. (She has visited this country twice.)
- Я здесь уже 2 часа. (I have been here for 2 hours.)
Слова маркеры Present Perfect
Слова-маркеры Present Perfect играют важную роль в построении предложений на английском языке. Они помогают нам указать на присутствие определенного действия или события в прошлом, которые имеют связь с настоящим моментом.
Одним из таких слов-маркеров является «already» (уже). Например: «I have already finished my homework» (Я уже закончил свою домашнюю работу). Здесь мы указываем, что закончили задание до настоящего момента.
Еще одним словом-маркером является «yet» (еще не). Например: «She hasn’t eaten lunch yet» (Она еще не поела обед). В этом случае мы говорим о том, что действие еще не произошло к текущему моменту.
Кроме того, часто используется слово-маркер «just» (только что) для выражения недавно завершенных действий. Например: «They have just arrived home» (Они только что приехали домой).
Нельзя забывать и о словах-маркерах, которые указывают на период времени до настоящего момента. Такими словами могут быть «since» (с тех пор) и «for» (в течение). Например: «I have known her since childhood» (Я знаю ее с детства) или «They have been friends for years» (Они друзья уже несколько лет).
Важно помнить, что использование слов-маркеров Present Perfect может отличаться в зависимости от контекста
Также стоит обратить внимание на правильное сочетание временных фраз с Present Perfect для передачи точного значения времени
Practice What You’ve Learned
Now that you know the differences, it’s time to put your knowledge to test.
Here are a few simple and short quizzes and exercises that test your understanding of these two tenses.
English-hilfen.de: This is a simple fill-in-the-blanks quiz where you have to choose the right word or phrase from a drop-down list. It’s a pretty good way to know if you’ve grasped the basics or not.
English Page: Another simple one, in this quiz you have to fill-in-the-blanks for a paragraph by using the right form of the verb. To make it easier, they also offer hints.
English Grammar Online: This site also summarizes the differences between the two tenses, followed by several in-depth exercises and three practice tests. Try these out once you’re confident enough.
AgendaWeb: Finally, if you’re feeling brave enough, you can try the exercises listed here. There are plenty of them so you can try solving them from time to time as revision or for extra practice.
You can also check out this YouTube video from Learn English With Rebecca to learn more about the differences:
Besides this list, you can also try to practice by watching these tenses in action. In other words, you should get a lot of exposure to English conversations and sentences. Carefully study phrases for when the tenses are used and see how the verbs are working with the other words around it.
This kind of practice is also pretty easy to do. You can read English books or magazines, listen to English music or watch English videos, TV shows and movies. Basically, you can consume any English media that would show natural-sounding sentences!
For a more guided approach, the language learning program FluentU can help show the present perfect and the past simple in context.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
Try FluentU for FREE!
I hope this post has cleared the confusion between the present perfect and the past simple tenses. Now you know how you can still use present tense to talk about a past event.
The good news is, the more you practice the better you’ll be. So be consistent and motivated about learning and you’ll be fluent in English before you know it!c
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
And One More Thing…
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials, as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word “searching,” you see this:
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Present Perfect или Past Simple: упражнения
- I ___ (call) you yesterday.
- She ___ (never, try) gymnastics.
- They ___ (invite) me to their party. That’s why I’m so happy now.
- I ___ (not, call) you last night.
- We ___ (finish) our work last Tuesday.
- I ___ (go) for a walk every day last winter.
- We ___ (not, see) each other since July of 2022.
- She ___ (just, invite) me.
- Jack ___ (see) a bird. He ___ (turn on) his phone and ___ (take a photo) of the bird. Then Jack ___ (send) the photo to all his friends.
- I’m sad because you ___ (not, tell) me your secrets.
Ответы:
- I called you yesterday. – Я позвонил тебе вчера.
- She has never tried gymnastics. – Она никогда не пробовала заниматься гимнастикой.
- They have invited me to their party. That’s why I’m so happy now. – Они пригласили меня на свою вечеринку. Поэтому я сейчас такой радостный.
- I didn’t call you last night. – Я не звонил тебе вчера ночью.
- We finished our work last Tuesday. – Мы закончили нашу работу в прошлый вторник.
- I went for a walk every day last winter. – Прошлой зимой я ходил гулять каждый день.
- We haven’t seen each other since July of 2022. – Мы не видели друг друга с июля 2022 года.
- She has just invited me. – Она только что пригласила меня.
- Jack saw a bird. He turned on his phone and took a photo of the bird. Then Jack sent the photo to all his friends. – Джек увидел птицу. Он включил свой телефон и сфотографировал эту птицу. Затем Джек отослал фото всем своим друзьям.
- I’m sad because you haven’t told me your secrets. – Я расстроен, потому что ты не рассказал мне свои секреты.
Past Simple vs Present Perfect
As present perfect and past simple are among the tenses in English that are confusing when it comes to application, we should understand the difference between past simple and present perfect clearly. The present perfect is used for actions that began in the past that have a connection to the present and the past simple is used for actions that have begun and ended in the past. The main difference between the two tenses is that while the present perfect has a connection to the present the past simple does not. This article attempts to clarify the usage of these two tenses while highlighting the differences between past simple and present perfect.
В чем отличия между Present Perfect и Past Simple?
“Ведь в русском языке такого нет”, – возмущаются все ученики. Конечно, нет, так как в русском языке есть совершенный (что сделал?) и несовершенный (что делал?) вид глагола. А в английском этого нет.
Так в чём же всё-таки разница между Present Perfect (подлежащее + have/has + Ved or V3 – I have done) и Past Simple (подлежащее + Ved or V2)?
Past Simple – Прошедшее простое
Так вот, условно говоря, то, что мы ДЕЛАЛИ в какой-то момент в прошлом (вчера, на прошлой неделе, месяц назад) – это факт в прошлом, никак с настоящим не связанный, это прошедшее простое.
Пример:
- What did you do yesterday?
- I did my homework and then I went to the gym.
Present Perfect – Настоящее совершенное
То, что мы СДЕЛАЛИ (НЕВАЖНО, КОГДА) и говорим о каком-либо результате в настоящем (фокус внимания не на действии в прошлом, а на результате в настоящем) – это настоящее перфектное. Have you done your homework?
Have you done your homework?
Yes. Here you are.
Учителю не важно, когда это происходило, ему важен результат в настоящем
Key Differences Between Past Simple and Present Perfect
Here are the basic differences between these two tenses:
- Time Specificity: The past simple is time-specific, while the present perfect is not.
- Relevance to Present: Present perfect actions are usually relevant to or affect the present; past simple actions do not.
- Time Markers: Past simple often uses specific time markers, while present perfect usually does not.
Essentially, we can think of it this way:
- For completed past actions and repeated actions in the past, use the past simple tense.
- For actions that began in the past and continue (or could continue) now, use the present perfect tense.
Here’s a simple overview of the differences:
The above explanation includes the past perfect tense. You can learn about the differences between present perfect and past perfect here.