Сравнение Intel Core 2 Duo E6550 и Intel Pentium III 1400
Сравнительный анализ процессоров Intel Core 2 Duo E6550 и Intel Pentium III 1400 по всем известным характеристикам в категориях: Общая информация, Производительность, Память, Совместимость, Безопасность и надежность, Технологии, Виртуализация.
Анализ производительности процессоров по бенчмаркам: PassMark — Single thread mark, PassMark — CPU mark, Geekbench 4 — Single Core, Geekbench 4 — Multi-Core, CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — Face Detection (mPixels/s), CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — Ocean Surface Simulation (Frames/s), CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — T-Rex (Frames/s), CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — Video Composition (Frames/s), CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — Bitcoin Mining (mHash/s).
Intel Core 2 Duo E6550
vs
Intel Pentium III 1400
Преимущества
Причины выбрать Intel Core 2 Duo E6550
- Процессор новее, разница в датах выпуска 5 year(s) 7 month(s)
- На 1 ядра больше, возможность запускать больше приложений одновременно: 2 vs 1
- Примерно на 66% больше тактовая частота: 2. 33 GHz vs 1.4 GHz
- Примерно на 4% больше максимальная температура ядра: 72°C vs 69°C
- Более новый технологический процесс производства процессора позволяет его сделать более мощным, но с меньшим энергопотреблением: 65 nm vs 130 nm
- Кэш L1 в 8 раз(а) больше, значит больше данных можно в нём сохранить для быстрого доступа
- Кэш L2 в 16 раз(а) больше, значит больше данных можно в нём сохранить для быстрого доступа
- Производительность в бенчмарке PassMark — Single thread mark в 3.3 раз(а) больше: 909 vs 272
- Производительность в бенчмарке PassMark — CPU mark в 4.6 раз(а) больше: 881 vs 193
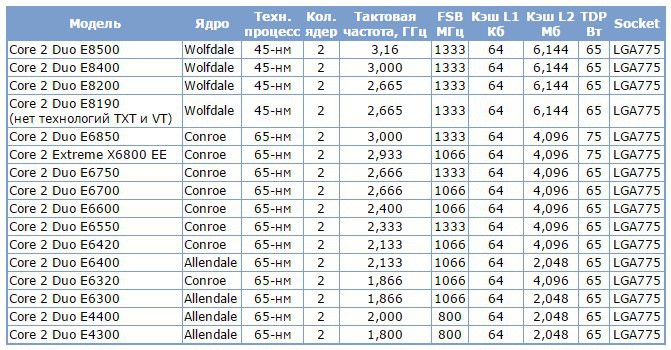
| Дата выпуска |
July 2007 vs December 2001
Количество ядер
2 vs 1
Максимальная частота
2.33 GHz vs 1.4 GHz
Максимальная температура ядра
72°C vs 69°C
Технологический процесс
65 nm vs 130 nm
Кэш 1-го уровня
64 KB vs 8 KB
Кэш 2-го уровня
4096 KB vs 256 KB
PassMark — Single thread mark
909 vs 272
PassMark — CPU mark
881 vs 193
Причины выбрать Intel Pentium III 1400
В 2. 1 раз меньше энергопотребление: 31.2 Watt vs 65 Watt
| Энергопотребление (TDP) |
31.2 Watt vs 65 Watt
CPU 1: Intel Core 2 Duo E6550CPU 2: Intel Pentium III 1400
| PassMark — Single thread mark |
| CPU 1 |
| CPU 2 |
PassMark — CPU mark
| CPU 1 |
| CPU 2 |
| Название |
|---|
Intel Core 2 Duo E6550
Intel Pentium III 1400
PassMark — Single thread mark
909
272
PassMark — CPU mark
881
193
Geekbench 4 — Single Core
303
Geekbench 4 — Multi-Core
527
CompuBench 1.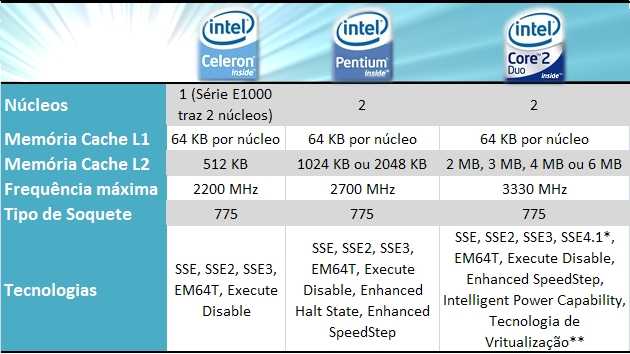 5 Desktop — Face Detection (mPixels/s)
5 Desktop — Face Detection (mPixels/s)
0.261
CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — Ocean Surface Simulation (Frames/s)
18.666
CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — T-Rex (Frames/s)
0.077
CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — Video Composition (Frames/s)
0.371
CompuBench 1.5 Desktop — Bitcoin Mining (mHash/s)
1.88
| Intel Core 2 Duo E6550 |
|---|
Intel Pentium III 1400
Название архитектуры
Conroe
Tualatin
Дата выпуска
July 2007
December 2001
Место в рейтинге
2924
2978
Цена сейчас
$14.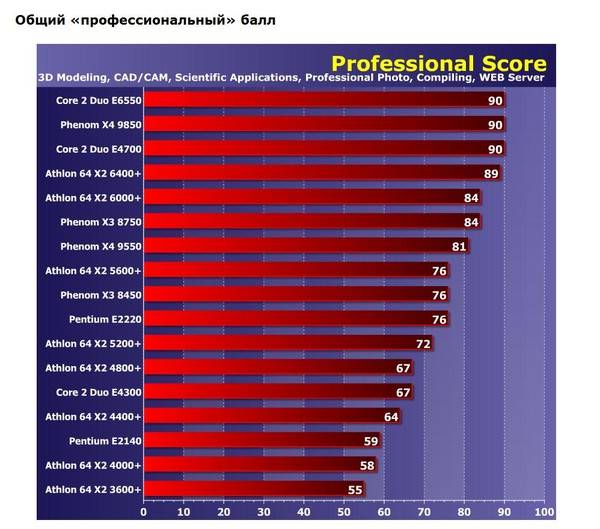 95
95
Processor Number
E6550
Серия
Legacy Intel Core Processors
Legacy Intel Pentium Processor
Status
Discontinued
Discontinued
Соотношение цена/производительность (0-100)
29.56
Применимость
Desktop
Desktop
Поддержка 64 bit
Base frequency
2. 33 GHz
1.40 GHz
Bus Speed
1333 MHz FSB
133 MHz FSB
Площадь кристалла
143 mm2
80 mm2
Кэш 1-го уровня
64 KB
8 KB
Кэш 2-го уровня
4096 KB
256 KB
Технологический процесс
65 nm
130 nm
Максимальная температура ядра
72°C
69°C
Максимальная частота
2. 33 GHz
33 GHz
1.4 GHz
Количество ядер
2
1
Количество транзисторов
291 million
44 million
Допустимое напряжение ядра
0.8500V-1.5V
1.5V
Максимальная температура корпуса (TCase)
69 °C
Поддерживаемые типы памяти
DDR1, DDR2, DDR3
Low Halogen Options Available
Максимальное количество процессоров в конфигурации
1
1
Package Size
37. 5mm x 37.5mm
5mm x 37.5mm
Поддерживаемые сокеты
PLGA775
PPGA370
Энергопотребление (TDP)
65 Watt
31.2 Watt
Execute Disable Bit (EDB)
Технология Intel Trusted Execution (TXT)
Технология Enhanced Intel SpeedStep
Чётность FSB
Idle States
Intel 64
Intel AES New Instructions
Intel Demand Based Switching
Технология Intel Hyper-Threading
Технология Intel Turbo Boost
Thermal Monitoring
Intel Virtualization Technology (VT-x)
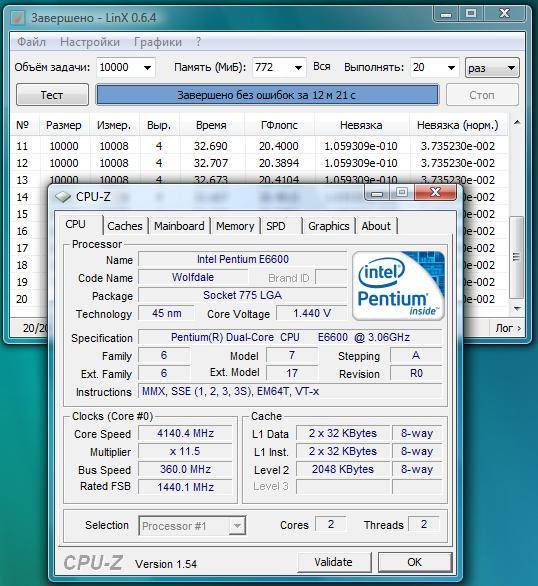
ASUS P5B Deluxe/WiFi-AP
Цена – $205/225
Чипсет Intel P965/ ICH8R
Слоты PCI-E 2×16, 1×1
Слоты PCI 3
Порты SATA 8 (6+2 eSATA)
Интерфейсы USB 2.0 (4+4), FireWire (2), PS/2, 2×Gigabit LAN
Аудио 7.1 (AD1988B)
Продукт предоставлен TechnoPark, www.technopark.kiev.ua
Отличное оснащение; хороший потенциал разгона; качественная компоновка; наличие FireWire
Довольно высокая цена; размещение разъемов памяти
Asus P5B Deluxe – наиболее функциональная модель от ASUS на новом наборе логики Intel. Компоновка платы выполнена на высоком уровне. Используется восьмифазная схема стабилизации напряжения питания процессора. Конструкция системы охлаждения, примененная на P5B Deluxe, становится традиционной для топовых материнских плат: радиатор, размещенный на северном мосту чипсета, посредством тепловой трубки соединен с охладителем элементов VRM, который покрыл лишь половину транзисторов (4 канала). Последние нагреваются не сильно, поэтому установка такой конструкции – скорее элегантный способ увеличить площадь радиатора для «укрощения» довольно горячего чипсета.
На плате размещены два разъема, физические размеры которых соответствуют PCI Express x16, однако только один из них работает в таком режиме, второй слот может функционировать в режимах лишь x2 или x4. Модель обладает хорошими перспективами разгона. Напряжение на памяти может быть увеличено до 2,45 В, на CPU – до 1,7 В, да и в «рацион» северного и южного мостов без проблем добавляются живительные вольты. С последними версиями BIOS частота FSB возрастает до 650 MHz, что, впрочем, смело отнесем к разряду излишеств. А вот настройки таймингов памяти скорее достаточны, чем широки.
В целом ASUS P5B Deluxe производит впечатление добротного функционального продукта с одним из лучших показателей разгона
Пользователям, планирующим организовать дома беспроводную сеть, рекомендуем обратить внимание на модификацию платы Asus P5B Deluxe/WiFi-AP, которая в дополнение к заслугам P5B Deluxe обладает еще и модулем IEEE 802.11g
Удвоение ядер не удваивает скорость
Многие компьютерные программы являются однопоточными, это означает, что их работа не может быть разделена между несколькими процессорами (CPU). Каждая из них должна работать с одним процессором (CPU). Это значит, что увеличение ядер не удвоит их эффективность. Если у вас есть однопоточное приложение, запущенное на четырехъядерном процессоре, то оно будет использовать только одно ядро, а остальные ядра в это время будут находиться в процессе ожидания, и только когда будут запущены другие приложения, они начнут действовать.
Правильное написание многопоточных приложений, которые можно масштабировать на нескольких процессорах одновременно, на самом деле является довольно сложной сферой компьютерной науки. Это становится все более актуальной проблемой, так как в будущем, скорее всего, будут появляться процессоры с большим количеством ядер, а не процессоры с меньшим числом ядер, рассчитанные на высокую скорость.
Некоторые приложения могут использовать преимущества нескольких ядер. Многопроцессорная архитектура Google Chrome позволяет ему выполнять действия с несколькими ядрами одновременно. Некоторые компьютерные игры также могут распределять расчеты на несколько ядер.
Тем не менее, большинство используемых приложений – однопоточные. Четырехъядерный процессор по сравнению с двухъядерным не будет работать с Microsoft Office вдвое быстрее. Если вы запустите Microsoft Office на разных процессорах, то увидите – производительность очень похожа.
Большое количество ядер может вам помочь, если вы хотите делать несколько задач одновременно или, если у вас есть многозадачные приложения, которые могут работать с многоядерными процессорами. Например, если вы запускаете несколько виртуальных машин во время кодирования видео, извлечения файлов, и некоторых других требовательных к процессору вещей, то восьмиядерный процессор может вам в этом помочь, в то время как даже четырехъядерный процессор начнет тормозить от таких нагрузок.
Performance comparison with the benchmarks:
| CPU-Z – Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 5561,511 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400T | 5621,493 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6600 | 4091,262 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6400 | 4221,191 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5600 | 4291,166 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5620 | 3951,136 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5500 | 3181,108 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5420 | 3771,094 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400 | 3311,079 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6500 | 3521,078 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 3821,077 |
| Intel Pentium G4620 | 3621,068 |
| Intel Pentium G4560 | 2921,028 |
| Intel Pentium G4600 | 3291,011 |
| Intel Pentium G4400 | 472956 |
| Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 | 258525 |
| Cinebench R15 – Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 214552 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400T | 218547 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5600 | 160435 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6400 | 165429 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5500 | 161410 |
| Intel Pentium G4620 | 154398 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5420 | 156398 |
| Intel Pentium G4600 | 153385 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400 | 151378 |
| Intel Pentium G4560 | 143364 |
| Intel Pentium G4500 | 181352 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 153325 |
| Intel Pentium G4400 | 140265 |
| Intel Pentium G3450 | 128263 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 6405U | 99260 |
| Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 | 101175 |
| Cinebench R20 – Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 5651,458 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400T | 5731,441 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5600 | 355966 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6400 | 374955 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5500 | 351911 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400 | 360894 |
| Intel Pentium G4600 | 317834 |
| Intel Pentium G4620 | 321830 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 390827 |
| Intel Pentium G4560 | 299761 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5420 | 290740 |
| Intel Pentium G3258 | 317624 |
| Intel Pentium G3450 | 284604 |
| Intel Pentium G3420 | 272545 |
| Intel Pentium G3240 | 198544 |
| Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 | 199346 |
| Cinebench R23 – Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 1,3853,823 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400T | 1,3963,789 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6400 | 9562,503 |
| Intel Pentium G4560 | 8612,340 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400 | 8972,227 |
| Intel Pentium G3258 | 9142,187 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 1,0272,179 |
| Intel Pentium G4620 | 8202,084 |
| Intel Pentium G4600 | 8152,083 |
| Intel Pentium G3450 | 7931,572 |
| Intel Pentium G3250 | 7071,402 |
| Intel Pentium G3260 | 6931,357 |
| Intel Pentium G3250T | 6701,314 |
| Intel Pentium E5400 | 6691,307 |
| Intel Pentium G2130 | 6131,259 |
| Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 | 450854 |
| Cinebench 2024 – Multi-Thread & Single Thread Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 83212 |
| PassMark – CPU Mark & single thread | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 3,0906,923 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400T | 2,5815,709 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 2,3715,504 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6605 | 2,6644,525 |
| Intel Pentium 6805 | 1,8274,436 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6600 | 2,5664,385 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6505 | 2,6414,367 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6405 | 2,5624,281 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6400 | 2,4794,233 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6500 | 2,4804,158 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5620 | 2,4134,113 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5600 | 2,2803,773 |
| Intel Pentium G4620 | 2,2533,756 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6405T | 2,1943,735 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400 | 2,2193,712 |
| Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 | 1,2331,151 |
| Geekbench 4 – Multi-core & Single Core Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 9,83219,907 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6500 | 4,8849,617 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5600 | 4,9179,543 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 5,0449,417 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6400 | 4,7489,193 |
| Intel Pentium G4620 | 4,6298,941 |
| Intel Pentium 6805 | 4,4968,722 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6600 | 4,5368,598 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5620 | 4,4398,547 |
| Intel Pentium G4600 | 4,2708,470 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5420 | 4,2888,436 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400 | 4,3688,404 |
| Intel Pentium G4560 | 4,1338,240 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5500 | 4,2948,208 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400T | 3,8597,557 |
| Intel Core 2 Duo E8400 | 1,8313,028 |
| Geekbench 5 – Multi-core & Single Core Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 1,4443,400 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400T | 1,2332,835 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 1,1292,452 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5620 | 1,0282,241 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6605 | 7342,228 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6400 | 1,0072,197 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5600 | 9742,183 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G6500 | 1,0102,163 |
| Intel Pentium G4620 | 8392,152 |
| Intel Pentium 6805 | 1,0172,084 |
| Intel Pentium G4560 | 9212,078 |
| Intel Pentium G4600 | 8432,076 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400 | 9212,045 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5420 | 9462,009 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5500 | 9101,914 |
| Geekbench 6 – Multi-core & Single Core Score | |
|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400 | 2,9706,453 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G7400T | 1,5733,435 |
| Intel Pentium Gold 7505 | 1,2392,923 |
| Intel Pentium 6805 | 1,3002,624 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5420 | 7661,675 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400 | 6691,652 |
| Intel Pentium G4620 | 7891,583 |
| Intel Pentium G4560 | 6921,548 |
| Intel Pentium G4600 | 7801,508 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5420T | 6851,459 |
| Intel Pentium Gold G5400T | 6301,231 |
| Intel Pentium G3240 | 5981,042 |
| Intel Pentium G3250 | 6141,026 |
| Intel Pentium G2130 | 5651,007 |
| Intel Pentium G3450 | 5841,001 |
Модели поступили в продажу
В таблице ниже показаны модели Pentium Dual Core, появившиеся на рынке. Многие из них имеют общие характеристики, несмотря на то, что основаны на разных ядрах; по этой причине, чтобы сделать эти сходства более очевидными и «облегчить» отображение, в некоторых столбцах отображается значение, общее для нескольких строк. Ниже также приведена легенда терминов (некоторые сокращенные), используемых для заголовков столбцов:
- Коммерческое название : означает название, под которым конкретный образец был размещен на рынке.
- Дата : означает дату размещения на рынке данного конкретного образца.
- Количество ядер : означает количество ядер, установленных в корпусе : 1, если «одноядерный», или 2, если «двухъядерный».
- Socket : разъем материнской платы, в который вставляется процессор. В этом случае, помимо названия, число также представляет собой количество контактных пинов .
- Clock : рабочая частота процессора.
- линька : означает «Множитель», то есть коэффициент умножения, на который необходимо умножить частоту шины, чтобы получить частоту процессора.
- Пр.Производ. : означает «Производственный процесс» и обычно указывает размер затворов транзисторов ( 180 нм, 130 нм, 90 нм) и количество транзисторов, встроенных в процессор, выраженное в миллионах.
- Вольтаг. : означает «Напряжение» и указывает напряжение питания процессора.
- Ватт : означает максимальное потребление данного конкретного экземпляра.
- Шина : частота системной шины.
- Кэш : размер кэшей 1-го и 2-го уровня.
- XD : расшифровывается как «XD-бит» и указывает на реализацию технологии безопасности, предотвращающей выполнение вредоносного кода на компьютере.
- : означает «EM64T» и указывает на реализацию 64-битной технологии Intel
- HT : расшифровывается как «Hyper-Threading» и указывает на реализацию эксклюзивной технологии Intel, которая позволяет операционной системе видеть 2 логических ядра.
- ST : сокращение от «SpeedStep Technology», которая представляет собой энергосберегающую технологию, разработанную Intel и включенную в последнюю серию Pentium 4 Prescott 6xx для ограничения максимального энергопотребления.
- VT : означает «Vanderpool Technology», технологию виртуализации, которая позволяет одновременно запускать несколько разных операционных систем .
- Core : означает кодовое название проекта, лежащего в основе этого конкретного экземпляра.
| Коммерческое название | Свидание | Разъем | № ядра | Часы | линька | Пр.Производ. | Вольтаг. | Ватт | Автобус | Кэш | XD | ХТ | СТ | ВТ | Основной | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Двухъядерный Pentium E2140 | 3 июня 2007 г. | 775 | 2 | 1,6 ГГц | 8x | 65 нм | 1,21 В | 65 Вт | 800 МГц | L1 = 2×64 КБ L2 = 1 МБ | Ага | Ага | Нет | Ага | Нет | Конро-Л |
| Двухъядерный Pentium E2160 | 1,8 ГГц | 9x | ||||||||||||||
| Двухъядерный Pentium E2180 | 26 августа 2007 г. | 2 ГГц | 10x | |||||||||||||
| Двухъядерный Pentium E2200 | 2 декабря 2007 г. | 2,2 ГГц | 11x | |||||||||||||
| Двухъядерный Pentium E2220 | 1-й кв. 2008 г. | 2,4 ГГц | 12x | |||||||||||||
| Двухъядерный Pentium T2060 | январь 2007 г. | М. | 1,6 ГГц | 12x | 0,7625 В-1,3 В | 31 Вт | 533 МГц | Нет | Ага | Йона | ||||||
| Двухъядерный Pentium T2080 | апрель 2007 г. | 1,73 ГГц | 13x | |||||||||||||
| Двухъядерный Pentium T2130 | середина 2007 г. | 1,87 ГГц | 14x |
Чем отличается Pentium Dual Core от Core 2 Duo?
Когда в продаже технологий остается всего пара игроков – они занимаются полным беспределом. Так, к примеру, Intel, имея единственного соперника AMD, разрешает себе дурить головы возможным покупателям, запутывая их в обширнейших линейках моделей собственных процессоров. Так, к примеру, похожие названия Pentium Dual Core и Core 2 Duo принадлежат абсолютно разным семействам процессоров, и упоминание Core и в том и другом случае привносит серьезный компонент путаницы при подборе системы или деталей.
Большинство до этого времени принимают данные модели за одну, полагая, что пентиумами называются те процессоры Intel, которые не Селерон, а dual и двойка – различные варианты написания. Посмотрим, насколько различные эти семейства процессоров в действительности.
Что такое Pentium Dual Core и Core 2 Duo
Сравнение Pentium Dual Core и Core 2 Duo
Отличие Pentium Dual Core от Core 2 Duo
Что такое Pentium Dual Core и Core 2 Duo
Pentium Dual Core – семейство двухъядерных процессоров для настольных систем от Intel, возникшее в 2007 году и позиционируемое изготовителем как решение для малобюджетных ПК. Процессоры выстроены на архитектуре Intel Core и монтируются в сокеты LGA 775.
Core 2 Duo – семейство двухъядерных процессоров, выстроенных на архитектуре Core. Обозначаются как замена Пентиумов, до возникновения Intel Core iХ ,были довольно востребованными процессорами в массовом сегменте.
Монтируются в сокеты LGA 775.
Сравнение Pentium Dual Core и Core 2 Duo
В чем практическая разница между Pentium Dual Core и Core 2 Duo? Кажется, два ядра на одной архитектуре, частоты – в зависимости от моделей, одновременное возникновение, другими словами фактически одинаковые линейки, впрочем Core 2 Duo – производительнее и, необходимо заметить, актуальнее.
Кэш второго уровня в данных моделях общий для двоих ядер (в то время соперник AMD в недорогих моделях уже его разделял, чем обеспечил более большой уровень свободы параллельных вычислений). Кэш второго уровня объемом в 2 Мб имеют лишь две модели.
Для Core 2 Duo Intel кэш разделила, и его объем ниже 2 Мб не опускался, зато по максимуму брали 6 Мб.
Если большинство Pentium Dual Core базируются на вариации ядра, получившей именование Allendale, то в Core 2 Duo приблизительно поровну Conroe, Allendale и Wolfdale. Техпроцесс для Пентиумов – 65 нм (кроме пары старших моделей E5300 и E5200), семейство Core 2 Duo предусматривает и 45 нм (для ядра Wolfdale).
Тактовые частоты параметром чтобы сравнить Pentium Dual Core и Core 2 Duo являться не могут – моделей много. Впрочем самый маленький порог для Пентиума – 1,6 ГГц, для Core 2 Duo – 1,8 ГГц.
Максимум, исходя из этого – 2,6 ГГц и 3,5 ГГц.
15 Differences Between Dual Core and Core 2 Duo Processor

1. Description
Dual core is the generic name of the processors that come with two cores in them on a single silicon chip.
On the other hand, the name core 2 duo is given by Intel to those processors that belong to their second batch of dual core CPUs.
2. Classification
The dual core processors come under the multi-core processor category.
However, in comparison, the core 2 duo processors fall under the category of extensive versions of dual core processors.
3. Performance
The dual core processors are much better in comparison to all other single core processors when it comes to performance.
On the other hand, the core 2 duo processors are better in terms of performance in comparison to the dual core processors due to their better overclocking ability.
4. Cache Memory
In general, the Level 2 cache memory of the dual core processors is 3 MB, while, in comparison, that of the core 2 duo processors is double than that, being 6 MB.
5. Overclocking Ability
In the dual core processors the overclocking ability is approximately 3.12 GHz.
On the other hand, you can overclock the CPU up to 4.0 GHz in a core 2 duo processor.
6. Nature
All core 2 duo processors are dual core processors as well but, conversely, all dual core processors are essentially not core 2 duo processors.
7. Cost
A dual core processor is much cheaper when you consider the available specs and speeds in the prevailing market. This is because the dual core processors are actually the relegated versions of the core 2 duo processors.
On the other hand, the cost of the core 2 duo processors is a bit on the higher side because these are the advanced versions of the dual core processors.
8. Execution
The dual core processors, just as the name signifies, execute all operations by using its two cores completely.
On the other hand, the core 2 duo processors can carry out several tasks at the same time due to its high overclocking ability and high clock speed.
11. Age
The dual core processor is older in comparison to the core 2 duo processors and supports an older technology which puts it at a disadvantageous position.
On the other hand, though the architecture in which two cores are on the same processor is vaguely the same, that of the core 2 duo processors is more modern and advanced than the dual core processors.
12. Heat Generation
The dual core processors produce less heat in comparison to other previous versions of them.
However, on the other hand, the core 2 duo processors produce even lesser heat when compared with the dual core processors.
13. Power Efficiency
The dual core processors consume little power due to its outstandingly low TDP making it more power efficient.
In comparison, the core 2 duo processors are not as power efficient as the dual core processors.
14. Maximum Thermal Design Power
The maximum Thermal Design Power or TDP of the dual core processors is significantly low at 15 watts.
On the other hand, with a maximum TDP of 65 watts, the core 2 duo processors are nowhere near the dual core processors.
15. Clock Speeds
The clock speed of the dual core processors is quite acceptable, being about 2.33 GHz in the best situations.
On the other hand, the core 2 duo processors in the higher end can attain a higher clock speed of up to about 3.33 GHz.
Dual Core vs Core 2 Duo
The difference between dual-core and core 2 duo processors is that dual-core processors contain two cores and the core 2 duo processor is the second version of a dual-core processor.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of comparison | Dual-core | Core 2 Duo |
|---|---|---|
| Cpu speed | 1200.05 MHz | 797.78 MHz |
| Pipeline storage | 20 | 14 |
| Bus speed | 200.0 MHz | 133.0 MHz |
| Clock Speed | 1.6 to 2 GHz | 1.86 to 3.0 GHz |
| L2 Cache | 1 MB | 2MB to 4MB |
What is Dual-core?
A silicon chip in the central processing unit has two cores and this is named as a Dual core. This is made to perform multiple tasking.
The Dual-core processor is manufactured by Intel as well as AMD. The performance of the previous versions of the processor is much less when compared to the dual-core processor.
In the previous versions, the power consumption is higher and the dual-core has very less power consumption. The next factor is the clock speed which is less in dual-core than in previous versions.
What is Core 2 Duo?
Core 2 duo is also a dual-core processor and the difference is the second batch of the dual-core processors is given this name. The core 2 duo processors are a little better as they are made in such a way that they can work on virtualization.
In this, the tasks that are given are executed separately as individual tasks because of the presence of two cores. Most of the machines don’t take advantage of the dual processors.
These processors changed the system performance when compared to the previous model. These processors are being used in desktops and laptops in a wide range at a lower price.
Main Differences Between Dual Core and Core 2 Duo
- The dual-core processors the number of cycles that a CPU can execute a task in a second is low. Whereas in the core 2 duo processor the CPU speed is faster which makes the core 2 duo run faster.
- Whenever there are instructions given to the processors, the instructions get accumulated in a pipeline and this is called the pipeline storage. In the dual-core, the pipeline storage is more than in the core 2 duo processor.
- During the processing, data is transferred or moved across the bus. The speed at which the data moves in a bus is called bus speed and in dual-core it is more than compared to the core 2 duo.
- The lower the clock speed the higher will be the performance of the processors as well as the computer. The dual-core has lesser clock speed when compared to the core 2 duo.
- The memory that is built in a processor is termed as L2 cache and this cache size is less in the dual-core processor than in the core 2 duo processors. So this made core 2 better than the dual-core processor.
- With a little difference between these two processors, the whole operating system, the software that is running and also the tasks that are being executed were changed and this brought a lot of changes in the way of working and development. The subset of the dual-core processors namely core 2 duo processors are running with better clock speed and bus speeds.
- As the single processors can perform lesser than the dual processors these dual-core processors and core 2 duo processors can execute the tasks at a higher rate. Later on, different generations of processor’s development took place which increased the performance of multitasking even high.
References
- https://arxiv.org/abs/0709.1861
Home – Hardware – Dual Core vs Core 2 Duo: Difference and Comparison
Last Updated : 11 June, 2023
One request?
I’ve put so much effort writing this blog post to provide value to you. It’ll be very helpful for me, if you consider sharing it on social media or with your friends/family. SHARING IS ️