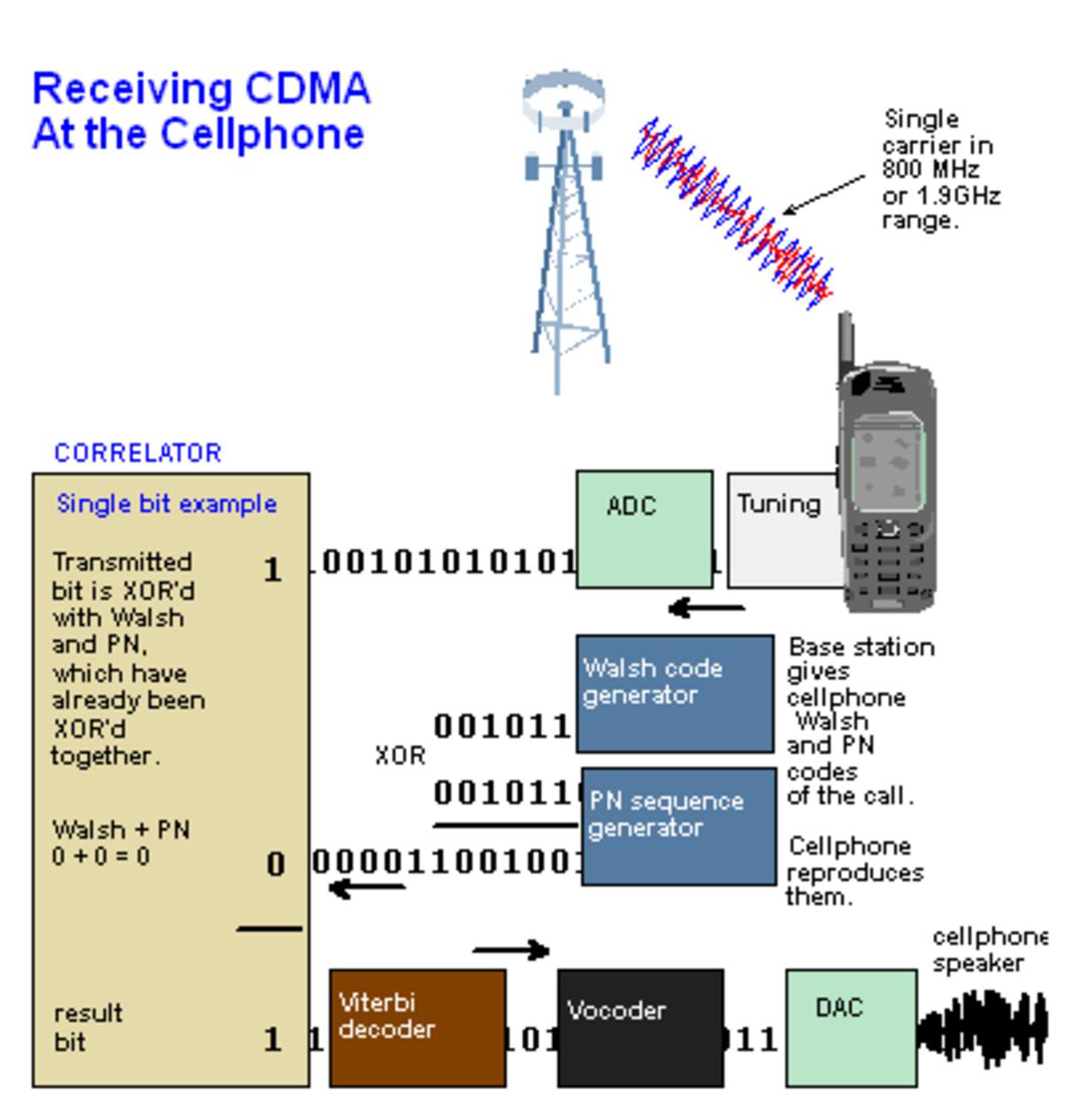
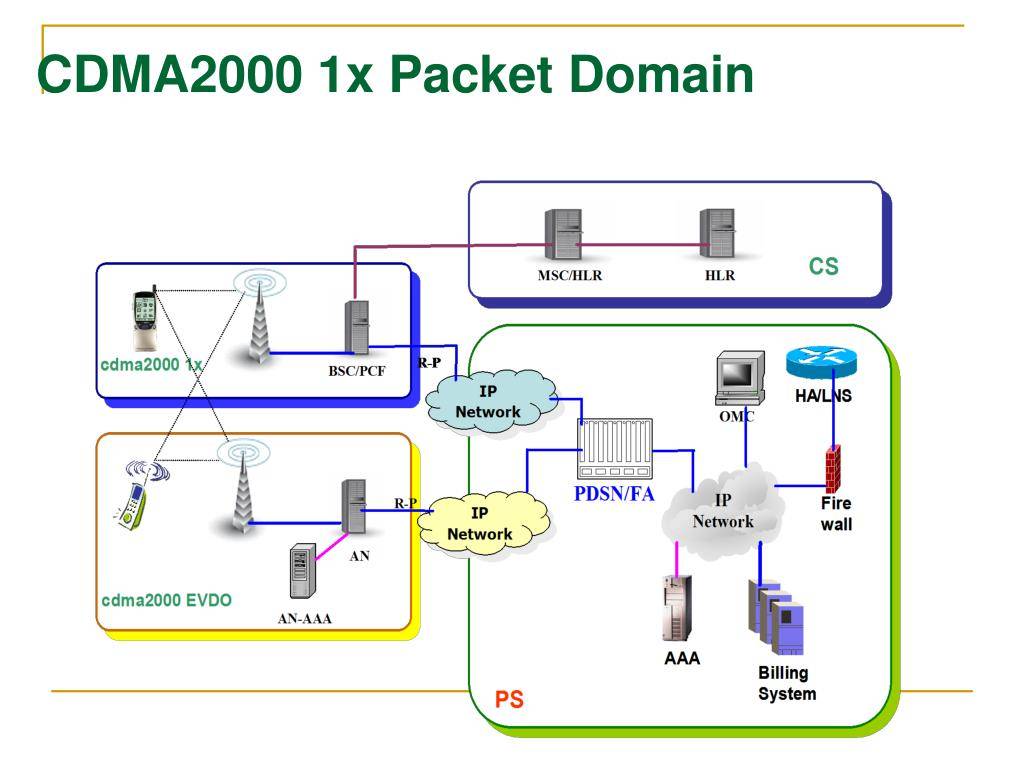
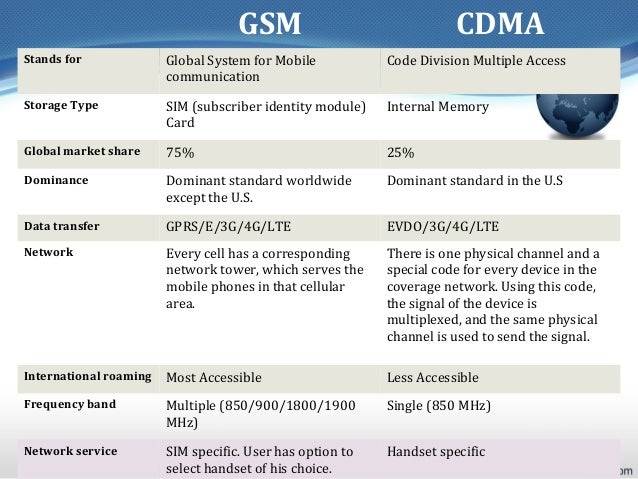
Заключительные мысли
GSM и CDMA совместимы только с сетями 2G и 3G соответственно. С появлением 4G все операторы приняли всемирный стандарт LTE. Там, где услуга LTE нестабильна или недоступна, в качестве резерва используются GSM и CDMA.
GSM позволяет одновременно передавать данные и голос, тогда как CDMA не поддерживает эту функцию. В отличие от CDMA, GSM позволяет пользователям передавать свои данные на новый телефон, вставив свою SIM-карту. В отличие от сетей CDMA, в которых разрешено использовать только телефоны утвержденных производителей, в сетях GSM могут работать любые совместимые телефоны.
Программы для Windows, мобильные приложения, игры – ВСЁ БЕСПЛАТНО, в нашем закрытом телеграмм канале – Подписывайтесь:)
What Is GSM?
If you look at the differences between GSM vs. CDMA from a consumer point of view, you will find that the major difference is that the GSM networks use SIM cards to store your data and enable users to make calls.
The SIM card holds data about the services available to the network subscribers in the same way a whitelist of CDMA phone numbers is working. You can easily change the GSM networks by simply getting a card by another GSM service provider and although some carriers do sell locked GSM phones you can switch providers more easily compared to CDMA networks, especially when travelling abroad.
Photo on Amazon
GSM networks rely on Time Division Multiple Access technology to transmit your voice conversations. TDMA assigns time slots to multiple conversation streams, then alternates them in sequence and switches between one conversation and another in short intervals. Data is being transmitted during these intervals and the network knows who are online by checking the available and connected SIM cards.
Различия с GSM технологией
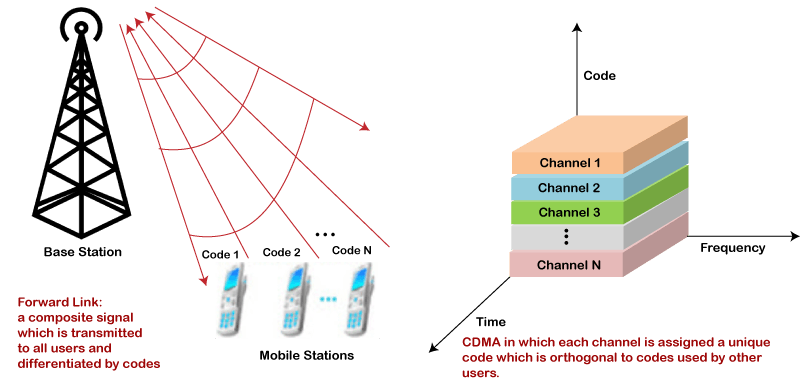
Мультиплексирование: В GSM используется временное мультиплексирование (TDM), а в CDMA используется мультиплексирование кодовых делителей (CDMA). Это означает, что в GSM разные пользователи разделяют доступ к каналу по времени, тогда как в CDMA разные пользователи передают данные одновременно, используя разные коды.
Спектральная эффективность: GSM более спектрально эффективна, чем CDMA. Это означает, что в GSM можно передавать больше информации на одной и той же частоте, чем в CDMA. В GSM используется FDMA (частотное мультиплексирование), что позволяет разделить доступ к каналу по частоте.
Расход энергии: CDMA обычно требует больше энергии для передачи данных, по сравнению с GSM. Это связано с использованием более сложных алгоритмов для передачи и декодирования сигналов.
Переносимость номера: GSM обеспечивает лучшую переносимость номера, чем CDMA. Это означает, что пользователь GSM может перенести свой номер телефона при переходе от одного оператора связи к другому, в то время как пользователь CDMA обычно не может перенести свой номер.
В целом, GSM и CDMA являются двумя разными технологиями передачи данных и голосовых сообщений. Каждая технология имеет свои преимущества и недостатки, и выбор между ними зависит от инфраструктуры оператора связи и предпочтений пользователя.
How GSM Technology works?
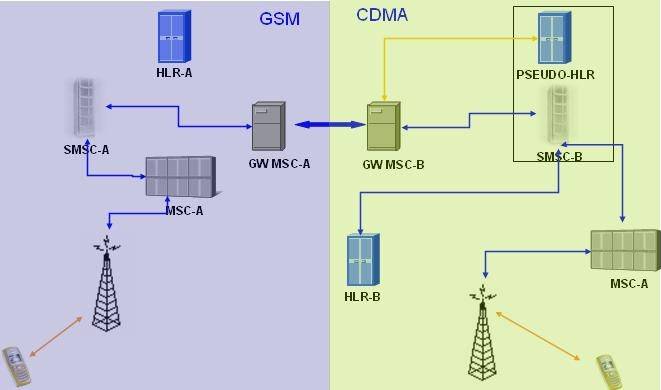
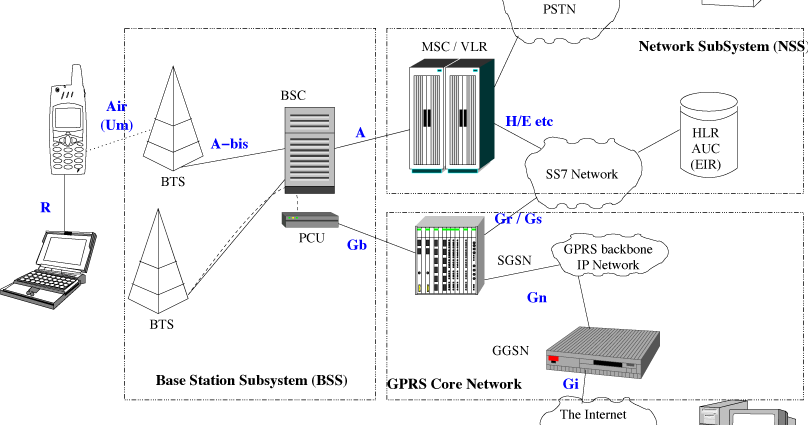
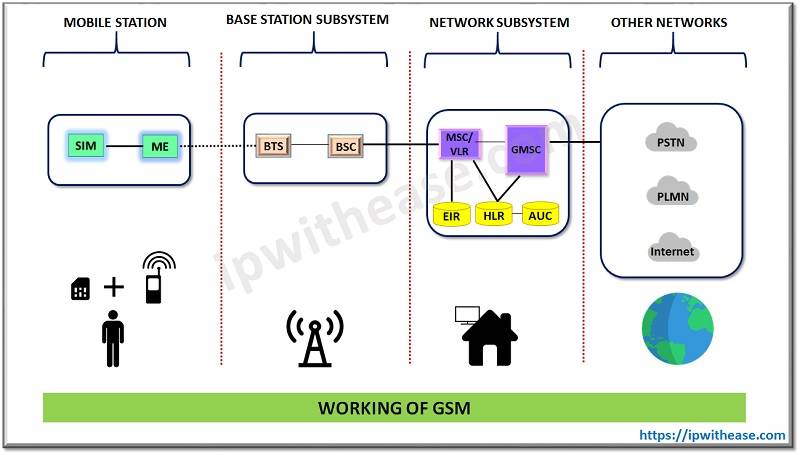
The main components of GSM system are – Network subsystem, Radio subsystem and Operation and maintenance subsystem.
Components of GSM :
- Network subsystem – perform call processing and subscriber related functions and it includes
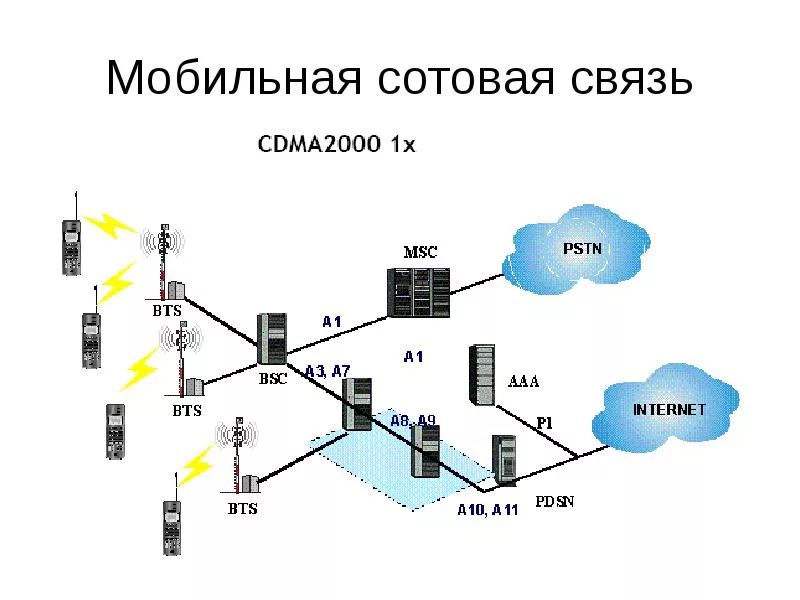
- MSC – Mobile switching Centre controls radio subsystem and it comprises of BSC (base station controller) and it is responsible for signalling to / from BTS, frequency allocation & power control. BTS (base transceiver station) maintains air interface , paging information, radio level power control, speech processing and handles ciphering functionality.
- HLR – Home location register contains subscriber details such as Subscriber ID (IMSI and MSIDSN), current location, subscriber status, authentication key, mobile subscriber roaming number
- VLR – Visitor location register provides local database for subscriber and contains copy of information (related to subscriber) stored in HLR.
- AuC – Authentication center used for authentication of a mobile subscriber into the network
- EIR – Equipment identity register stores International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) numbers and it is specific to handset
- GMSC – gateway MSC is a used to route calls outside the mobile network
GSM and CDMA Definitions
GSM allows for easy international roaming and compatibility across various networks.
GSM’s international roaming capabilities made it the preferred choice for travelers.
13
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
CDMA
CDMA technology encrypts each call using coded signals over the full available spectrum.
CDMA’s encryption method made it a secure choice for mobile communication.
12
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
ADVERTISEMENT
GSM is a mobile network standard widely used internationally.
Her GSM phone worked seamlessly when she traveled to Europe.
8
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
CDMA
CDMA phones do not require a SIM card, connecting to the network directly.
When she bought her CDMA phone, it had to be activated by the carrier.
11
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
GSM devices can be easily unlocked and used with different network providers.
After unlocking her GSM smartphone, she switched to a different carrier.
7
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
CDMA
CDMA is known for its capacity to support more users per MHz of bandwidth.
CDMA efficiently managed network traffic during peak hours.
8
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
GSM technology supports voice calls, SMS, and data services.
GSM networks provided the backbone for the massive growth of mobile communication.
7
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
ADVERTISEMENT
CDMA
CDMA is a channel access method that allows multiple users on the same frequency.
His CDMA phone provided excellent call quality even in rural areas.
5
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
GSM networks utilize a SIM card to identify and authenticate subscribers.
He transferred his GSM SIM card to a new phone to keep his contacts and number.
6
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
CDMA
CDMA was primarily used by carriers in the United States before the shift to LTE.
CDMA carriers in the U.S. have mostly transitioned to newer LTE technology.
5
Shumaila SaeedNov 10, 2023
An international telecommunications standard for the transmission of voice and data between cellphones and other mobile devices.
Shumaila SaeedNov 09, 2023
Методы передачи данных в GSM против CDMA
Другое различие между GSM и CDMA заключается в способах передачи данных. Технология высокоскоростной беспроводной передачи данных GSM, GPRS (общая служба пакетной радиосвязи), обычно предлагает более медленную полосу пропускания данных для беспроводного подключения к данным, чем высокоскоростная технология CDMA (1xRTT, сокращение от технологии радиопередачи с одной несущей), которая имеет возможность обеспечения ISDN (цифровая сеть с интеграцией служб) – скорость до 144 Кбит / с (килобит в секунду). Однако для использования 1xRTT требуется выделенное соединение с сетью, в то время как GPRS отправляет пакеты, что означает, что вызовы данных, сделанные на телефоне GSM, не блокируют голосовые вызовы, как на телефонах CDMA.
GSM vs CDMA: Main Differences
GSM and CDMA are two different types of cellular networks. To explain the main difference between them, let us consider a simple analogy. Imagine a room full of people who want to talk to each other. If everyone starts talking at the same time, no one will be able to hear anything. To avoid confusion, there are several techniques that can be used, such as:
- People could take turns speaking (time division multiple access, or TDMA).
- People could speak at different pitches (frequency division multiple access, or FDMA).
- People could speak in different languages (code division multiple access, or CDMA).
CDMA is a more efficient way of using the available frequency spectrum than TDMA or FDMA. This is because CDMA allows multiple users to share the same frequency band at the same time, without interfering with each other.
Some other aspects of GSM and CDMA that customers should consider include:
- Connectivity: GSM phones use SIM cards to connect to the network, while CDMA phones do not. This means that if you want to change your GSM phone, you can simply insert your SIM card into a new phone. However, if you want to change your CDMA phone, you will need to contact your service provider and have them deactivate your old phone before you can activate your new one.
- Network coverage: GSM is the more widely used standard, with coverage in over 193 countries and territories. CDMA is more popular in North America, Japan, and some other parts of the world.
- Call quality: CDMA is generally considered to have better call quality than GSM. This is because CDMA is less susceptible to interference from other signals.
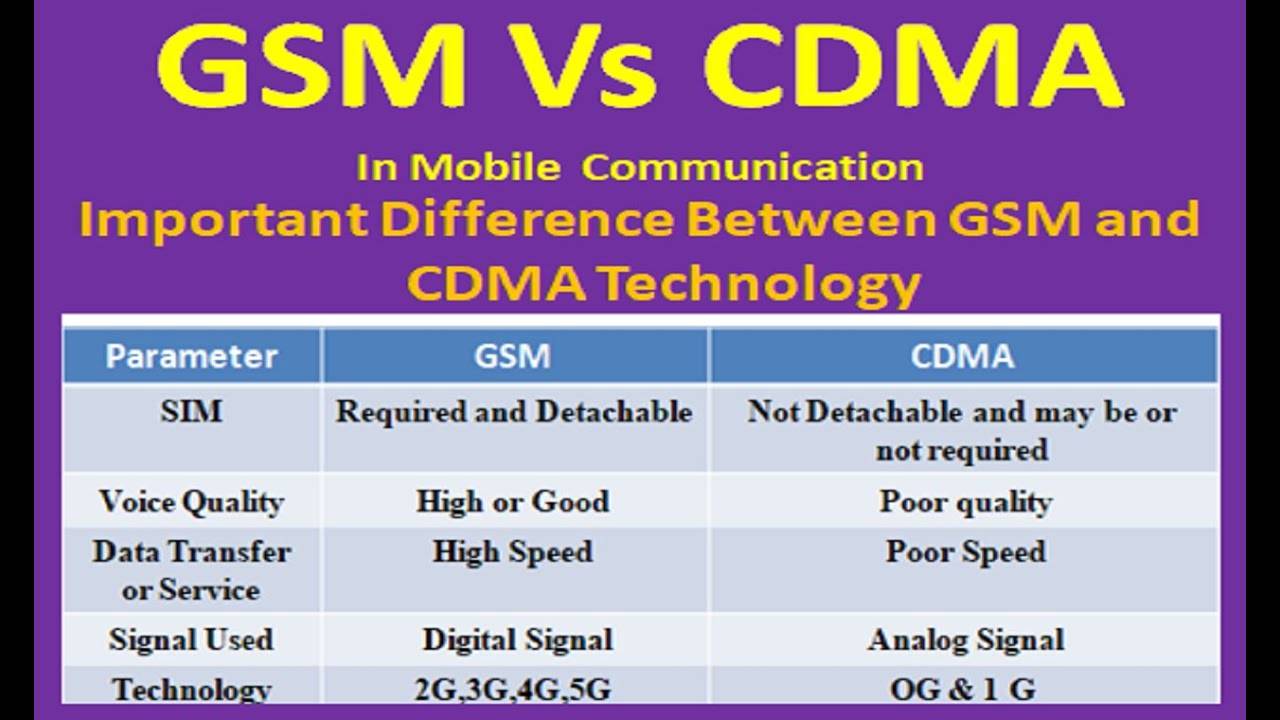
CDMA vs GSM: Comparison Chart:
| Feature | CDMA | GSM |
| Technology | Code Division Multiple Access | Global System for Mobile Communications |
| Developed by | Qualcomm | European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) |
| Popularity | More popular in North America, Japan, and some other parts of the world | More widely used standard, with coverage in over 193 countries and territories |
| Connectivity | Phones do not use SIM cards | Phones use SIM cards |
| Network coverage | Less widespread | More widespread |
| Call quality | Generally considered to have better call quality | Generally considered to have lower call quality |
| Security | Better security against eavesdropping | Less secure against eavesdropping |
| Battery life | Shorter battery life | Longer battery life |
| International roaming | Not possible with all carriers | Possible with all carriers |
| Switching phones or service providers | More difficult | Easier |
| SIM backup options | Not available | Available with some carriers |
Ultimately, the best type of cellular network for you will depend on your individual needs and preferences. If you travel frequently, GSM may be the better option because of its wider coverage. If you are concerned about call quality, CDMA may be a better choice.
Key Differences Between GSMA and CDMA
- The basic difference between GSM and CDMA is that the GSM is a SIM specific i.e. a mobile phone is identified in the network by the removable SIM inserted in that phone. On the other hand, in CDMA the network identifies a handset by the information stored in the internal memory and hence, its handset specific.
- The technology used in GSM to identify multiple callers in a channel is TDM and FDM. On the other hand, the in CDMA, multiple callers in a channel is separated by the code (CDM).
- The network tower serves all the mobile phone in a network cell in GSM. However, in CDMA there is a physical channel and a dedicated code for each cell in the network.
- In GSM voice and data can be transmitted simultaneously whereas, CDMA can not.
- As GSM is used and accepted worldwide it has roaming accessibility whereas, due to less use and acceptable worldwide CDMA has less accessibility.
- GSM uses GPRS which provide lower data bandwidth hence, it has the slower data transmission rate. On the other hands, CDMA uses EVDO which provide higher data bandwidth hence it has faster data transmission rate.
What you NEED to know about CDMA vs. GSM vs. LTE
Call Quality on CDMA vs. GSM
Whether you use a CDMA or GSM network, it does not matter. What matters is the coverage from the CDMA and GSM networks. Luckily, US Mobile has excellent cellular coverage using the best GSM and CDMA networks in the US.
CDMA vs. GSM phones
Switching GSM phones between different networks is easier than with CDMA phones. That’s because all GSM phones use removable SIM cards. You can put a SIM from one phone into a newer one, and all your info like phone number and plan will go to the new phone.
CDMA phones didn’t use SIMs. They used embedded serial numbers to identify their users to carriers. This meant three things:
- You couldn’t switch phones easily. You had to tell your carrier that you have a new phone so they can link the serial number of the new phone to your account.
- This gives carriers more control over their phone choices. And, more often than not, they didn’t accept new phones unless you bought them through them.
- Since there was no way to insert a SIM card, you could not take your phone with you to a GSM carrier.
LTE phones need SIM cards. And, since LTE provides the fastest data, most newer phones also have LTE capabilities. Thus, most newer phones also take SIM cards. Does that mean you can switch phones between carriers? It will be easier, but you still have to make sure your phone has different frequency bands. Or buy phones that support CDMA, GSM, and LTE on most bands.
Or find a carrier who provides service on GSM, CDMA, and LTE networks, lets you bring any phone and helps you figure out the best network for your phone (seriously, just ask us, and we’ll help), and provides great service and coverage with that
CDMA vs. GSM
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communication, and CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. GSM is considered the worldwide standard for cellular telephone communication. On the other hand, CDMA is regarded as the most secure telephonic network. Both the technologies differ by the process through which calls and data are sent over the respective systems.
Let us compare the two technologies to understand which one is better.
Technology
- Spread spectrum technology is used in CDMA for properly utilizing the available bandwidth. It lets the users transmit signals over the complete frequency spectrum.
- On the other hand, GSM works on a wedge spectrum that is known as a carrier. This is partitioned into several time slots where each slot is allocated to a user.
- This is done so that no other subscriber can access the slot until the current call is completed.
- GSM is much more in use than CDMA across the globe.
SIM cards
- GSM phones require a SIM card that has the personal information of the user and can be used in another device without the data being lost.
- There are no SIM cards in CDMA phones, but they use ESN (Electronic Serial Numbers). To activate such ESN enabled phones, you have to call the carrier or go online to do it.
- ESN based phones are not so popular among users, as most of them prefer SIM-based phones. Therefore, GSM beats CDMA here as well.
Security
- CDMA is highly secure as it has inbuilt encryption facilities. Here you will get a unique code, and all your conversations will be encoded. This makes it difficult for outsiders to trace the signal and intercept the calls.
- In GSM, temporary identification numbers are allocated to the user to secure the user’s numbers. Frequency hopping and encryption algorithms are used to protect the confidentiality of the conversations.
- Here, CDMA beats GSM as its security algorithms are powerful.
Global Coverage
- GSM is the most used mobile network in the world, having where more than 80% of users choose it over other networks. As international roaming is free in GSM, users prefer this over CDMA. It can be 3G devices but has faster data transfer speeds than CDMA.
- Most of the users of CDMA are in Japan, Canada, and the USA. However, the facility does not work in Europe. In the rural areas of North America, CDMA is more popular than GSM.
- Therefore, due to its worldwide coverage and popularity, GSM is better than CDMA.
Exposure to Radiation
GSM based phones emit 28 times more radiation as compared to CDMA phones. Continuous exposure to radiation can affect your health. So, CDMA phones are considered safer than GSM.
Let us dive into the details of the two technologies.
Specifications Between GSM and CDMA

| GSM | CDMA | |
| Networks | AT&T & T-Mobile | Sprint & Verizon |
| Compatibility | Worldwide | United States |
| Customer Information & Number | Is stored on SIM card | Is stored on the Networks database |
| Switching Companies | Transfer plans and get the company’s SIM card. You may use any unlocked device that is GSM compatible. | Transfer plans and get the company’s SIM card. Must use their branded devices. |
| Switching Phones | Insert SIM card into GSM device and it will host your number.GSM networks must accept all GSM compatible devices. | 1 – Carrier must agree to the switch and perform it.2 – CDMA networks are very specific in which devices they allow. Often limited to devices they sell. |
What’s the Difference Between EVDO, HSPA, and HSPA+?
EVDO, HSPA, and HSPA+ are mobile broadband technologies. Meaning, these technologies make accessing the internet through your phone possible. 3G CDMA networks utilize EVDO, while 3G GSM networks use HSPA and HSPA+. The differences between EVDO and HSPA are how they work and the speeds they can achieve.
What is EVDO?
EVDO is the mobile broadband technology used by the 3G CDMA network. Basically, EVDO enables carriers that utilize the 3G CDMA network to provide their mobile devices with high-speed internet access.
EVDO separates voice services from data services to maximize data transfer and provide high-speed internet access. In other words, voice and data operate on different frequency channels. As a result, voice and data cannot be used simultaneously. Meaning, that you won’t be able to access the internet or any data tools while you are talking on the phone.
When EVDO was adopted, under perfect conditions, it could achieve download speeds up to 2.4 Mbps and upload speeds of 153 Kbps. Most users would experience download speeds of 400-700 Kbps. Revisions were later made to improve data rates. With Revision A (Rev. A), EVDO’s download speeds improved to 3.1 Mbps, and upload speeds improved to 1.8 Mbps. Revision B (Rev. B) drastically enhanced the data speeds; it provided maximum download speeds of 14.7 Mbps and maximum upload speeds of 5.4 Mbps.
What is HSPA and HSPA+?
HSPA is the mobile broadband technology used by the 3G UMTS network. HSPA is composed of two different protocols: High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) and High-Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA). These technologies enhanced the original 3G data rates of 2 Mbps downlink and 128 Kbps uplink, to 14.4 Mbps downlink and 5.8 Mbps uplink.
In 2008, HSPA+, an improved version of HSPA, was introduced. It enhanced the 3G UMTS network even more. With HSPA+ data rates could reach up to 42 Mbps downlink and 11.5 Mbps uplink. Since HSPA+ couldn’t quite hit 4G speeds, it’s also known as 3.5G.
Unlike EVDO, HSPA and HSPA+ are able to transmit voice and data simultaneously.
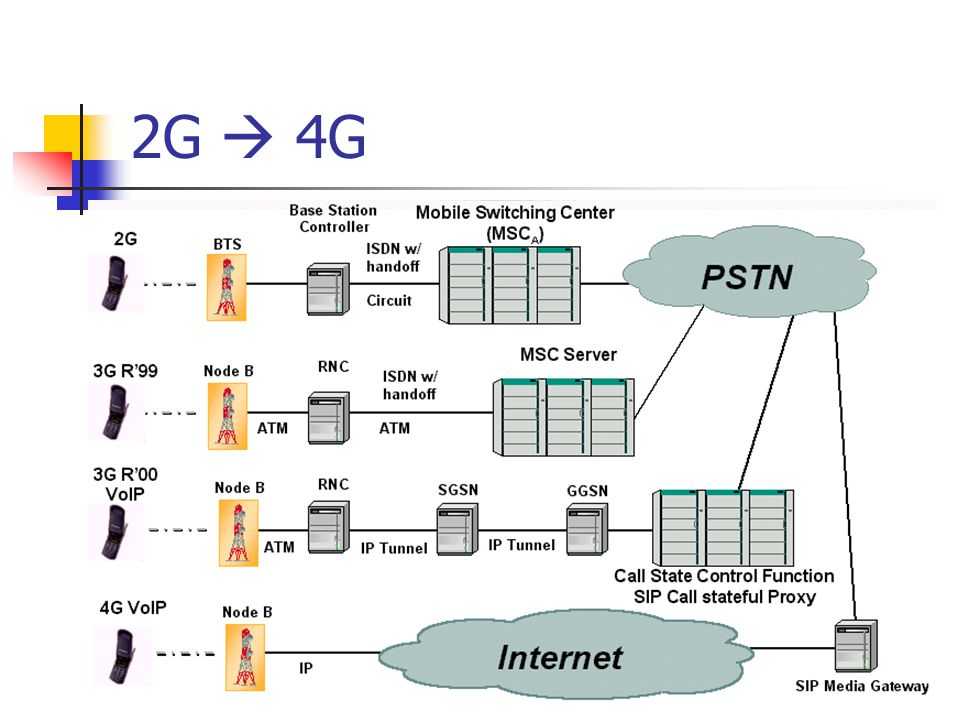
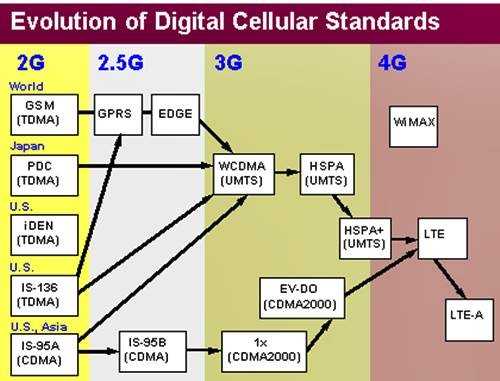
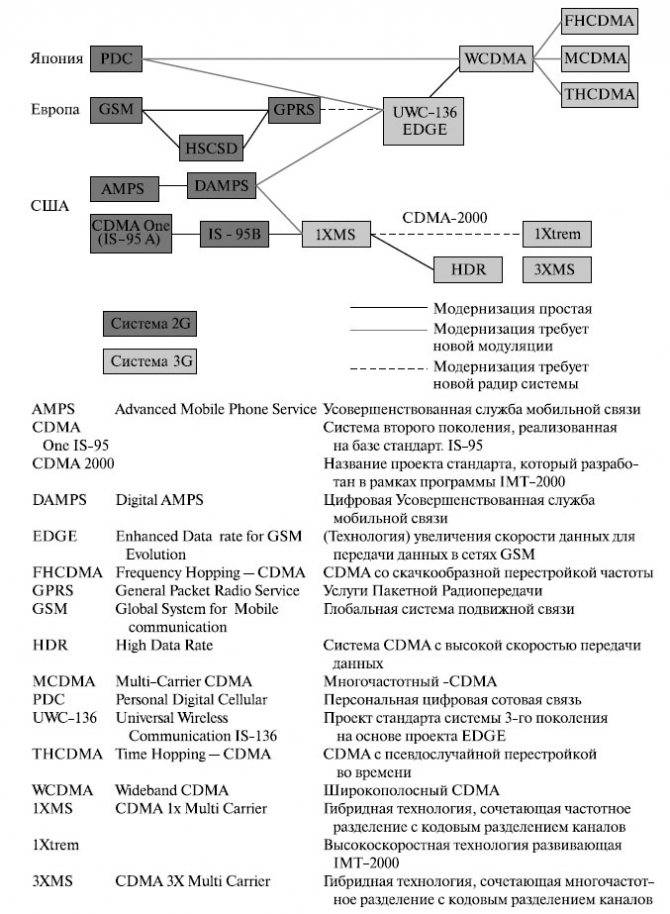
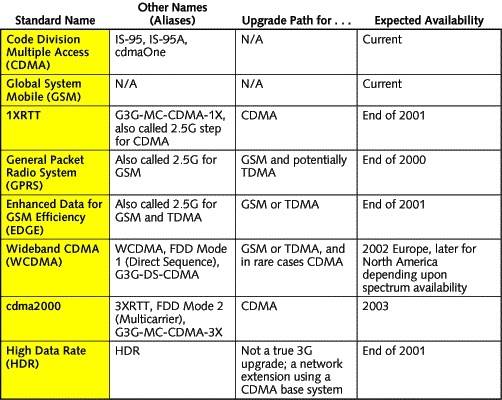
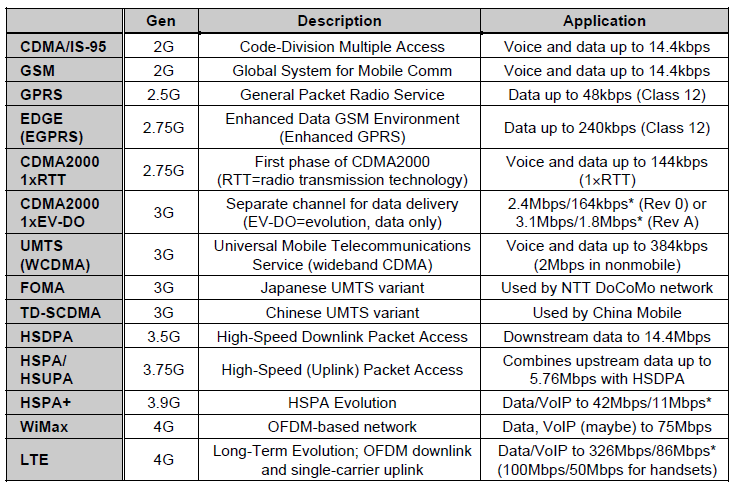
Difference Between GSM, UMTS, CDMA, CDMA2000, and LTE
GSM/UMTS, CDMA/CDMA200, and LTE are mobile standards that were developed to work with different networks. GSM and CDMA were used to move into the 2G network, while UMTS and CDMA2000 were used to transition into the 3G network. LTE, on the other hand, migrates CDMA/CDMA2000 and GSM/UMTS into the 4G network.
Since LTE pushes CDMA/CDMA2000 and GSM/UMTS networks into the next generation, it’s seen as the first step into streamlining the network. It was designed to increase the capacity, speed, and throughput of the mobile network.
LTE allows us to make phone calls, send text messages, browse the web, stream high-quality videos, and play games. To fulfill all of these demands with low latency and high speeds, LTE uses different technologies to transmit information from a cell site to a mobile device (known as downlink), and to transmit information from a mobile device to a cell site (known as uplink). It utilizes Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) for the downlink and Single Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) for the uplink. These technologies improved the channel compacity to allow more people to send and receive information at fast speeds.
Due to the technologies it uses, the LTE network offers a maximum download speed of 300 Mbps and a maximum upload speed of 75Mbps. Enhancements were later made to the 4G LTE standard and speed improved. LTE Advanced offered download speeds up to 1Gbps and LTE Advanced Pro supported download speeds up to 3 Gbps.
What’s the Difference Between UMTS and CDMA2000?
UMTS and CDMA2000 were used to transition from the 2G network to the 3G network – one was designed to work alongside GSM, while the other works with CDMA. UMTS was developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and CDMA2000 was developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP2). They are both part of the International Telecommunications Union’s IMT-2000 standard sets, which is a fancy name that represents a family of 3G cellular standards.
What is UMTS?
UMTS is the 3G standard for the GSM network.
UMTS uses Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (W-CDMA) to increased voice capacity and provide faster speeds. The 3G GSM network does not use FDMA or TDMA technology to transmit information like 2G GSM; it uses CDMA technology. The people using the 3G GSM network are no longer given time slots to share a frequency channel.
The UMTS payphone room would look very similar to the CDMA payphone room. Each data transmission would be protected by a unique code that can only be unlocked by the receiver.
Since the GSM technology was very different from what 2G GSM used, new base stations and new frequency allocations were needed to support UMTS technology.
This new standard offered download speeds up to 2 Mbps and upload speeds of 128 Kbps. Later HSPA was integrated into the mobile standard, followed by HSPA+. HSPA increased download speeds up to 14.4 Mbps, while HSPA+ increased download speeds up to 42 Mbps.
What is CDMA2000?
CDMA2000, also known as CDMA2000 1xRTT or IS-2000, is the 3G standard for the CDMA network. It’s based on CDMA technology to allow multiple users to use the same frequency channel at the same time. Each transmission is encrypted with a key that can only be deciphered by the receiver.
Voice and data services use different technologies. Voice uses CDMA2000 1xRTT technology, while data uses CDMA2000 EVDO.
1xRTT (Single Carrier Radio Transmission) was the first type of CDMA2000 technology. Compared to 2G CDMA, CDMA2000 1xRTT doubles the network voice capacity so that more people could talk on the phone at the same time. Under perfect conditions, 1xRTT provided data rates up to 153 Kbps, with real-world data rates averaging between 80 to 100 Kbps. Its successor, 1x Advanced, provided up to four times greater capacity.
EVDO focuses on implementing high-speed data rates for the CDMA network. This technology increased data rates up to 2.4 Mbps, and with later revisions, it increased to 3.1 Mbps. Keep in mind that EVDO only addresses data, not voice. To work, it needed a specific frequency channel, which was separated from the voice network. As a result, voice and data cannot be used simultaneously.
Стандарты и спецификации
Стандарт GSM базируется на использовании SIM-карт, которые идентифицируют абонента и сохраняют его контактную информацию. CDMA, напротив, использует электронную версию SIM-карты, называемую R-UIM (Removable User Identity Module).
Одной из главных различий между GSM и CDMA является способ передачи данных. В GSM передача данных осуществляется последовательно (через временные интервалы), а в CDMA данные передаются одновременно, используя различные коды.
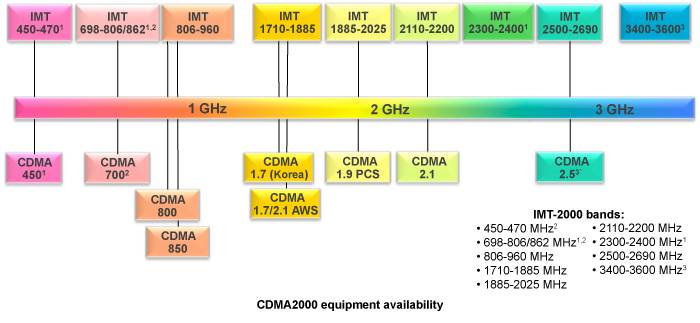
Кроме того, GSM и CDMA имеют разные частотные диапазоны. GSM работает в двух основных диапазонах: 900 МГц и 1800 МГц (или 850 МГц и 1900 МГц в Северной Америке). CDMA, с другой стороны, использует широкий диапазон частот, который может варьироваться в разных странах.
В заключение, разница между GSM и CDMA заключается в их технических спецификациях и способе передачи данных. Оба стандарта имеют свои преимущества и недостатки, и выбор между ними зависит от потребностей и предпочтений пользователя.
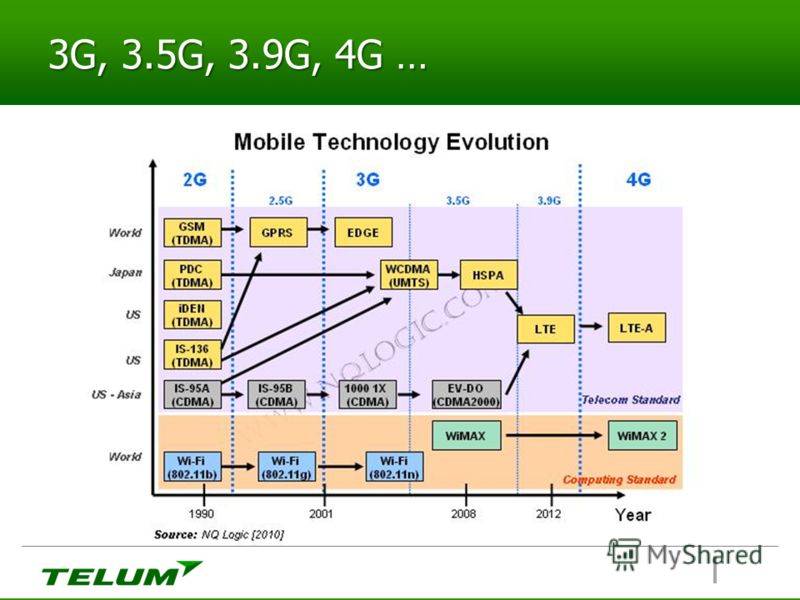
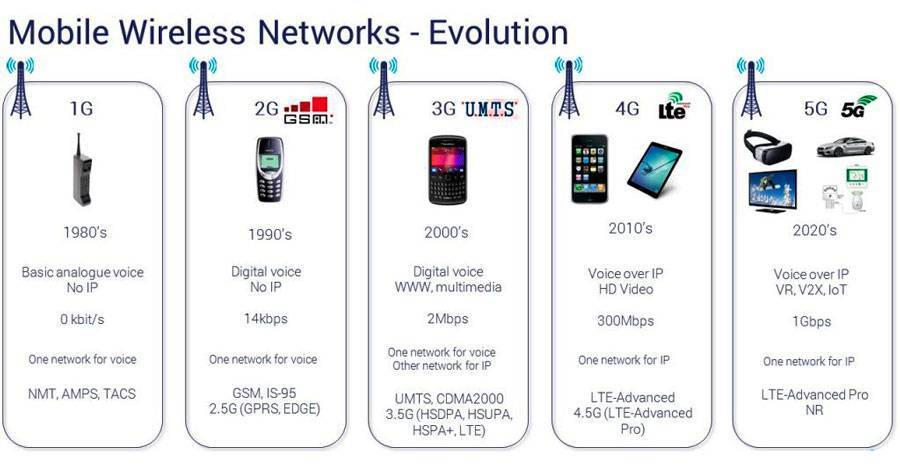
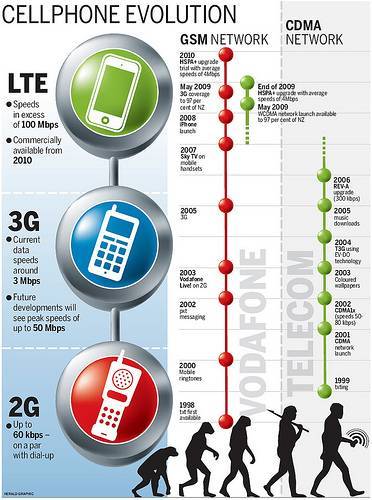
1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G
When cell phone providers talk about a “G,” they mean a generation of wireless technology. Each generation is able to support more users and has better data transfer capabilities.
The first generation was analog cellular phones. When carriers switched to 2G digital systems in the 1990s, they chose among several competing options; some of them died out, but CDMA and GSM are the two 2G camps that survived. They remained split during the ’00s through the third generation of cellular, which added better data speeds but stayed incompatible.
The CDMA/GSM split ended, in theory, as carriers all switched to LTE, a single, global 4G standard, starting in 2010. But the difference remained because phones still needed to access the older 2G and 3G networks, primarily for voice calls. AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon all started to phase in voice calling over 4G in 2014, but it took a while. All four carriers now support voice over 4G.
Now carriers are installing 5G, which (after a few false starts) will be a single global standard called 5G-NR. 5G is still in the early stages. You can’t make voice calls over it quite yet, and it doesn’t have true nationwide coverage. But 4G LTE is very mature now, and if you’re still on 2G or 3G, you should have no concerns about upgrading to a 4G-compatible phone.
The Samsung Galaxy S20 and its siblings were the first all-carrier 5G phones for the US
Why Carriers Are Shutting Down 2G and 3G
Everyone’s scrolling, Snapping, texting, FaceTiming, and more. Demands for mobile data use continue to rise. 2G and 3G, CDMA and GSM, are inefficient uses of the airwaves. 4G and 5G compress more information into each hertz of airwaves, and can combine channels much more flexibly for more efficient operation. So the carriers are retiring the older, less efficient technologies in exchange for newer networks which make better use of a scarce resource.
The carriers believe that most people have already switched to 4G through the natural process of upgrading phones. Phones making 4G voice calls have been in the market for years now. Apple’s first iPhone with 4G voice was the iPhone 6, from 2014. While it’s annoying to have to switch out an older phone because of this network transition, it’s far from sudden.
There’s no technological difference between “CDMA” and “GSM” carriers any more in the age of 4G LTE and 5G. Some cultural differences remain, though.
Specifically, Verizon makes it really hard to move your SIM card between devices without their permission, while it’s easier to do so on AT&T and T-Mobile. That’s an option in 4G. Verizon does it because historically, with CDMA, it could control which phones were on its network, and it wants to keep as much of that control as possible. AT&T and T-Mobile don’t in part because in the GSM era, the GSM spec meant they had to accept anyone with a compatible phone.
What is GSM?
GSM is a network that is commonly used in Europe and other regions of the world by mobile phone users. The GSM initials stand for Global Systems for Mobile Communications.
It was officially launched in 1991 in Finland, with an initial frequency band of 900MHz.
It uses Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Dimension Multiple Access (TMDA) technologies to provide its signal to its mobile phones and users.
The GSM is part of the evolutions of mobile wireless technologies such as General Packet Radio Services (GPRS), High-Speed circuit-Switched Data (HSCSD), Universal Mobile Telecommunications Services (UMTS), and Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE).
Even more interesting, in 2010, the GSM represented almost 0.8% of the worldwide market.
You May Like: What’s the Meaning of a GSM Unlocked iPhone?
Contact Us
Wilson Amplifiers is a leading provider of cell phone signal boosters, devices that amplify 5G (on select frequencies), 4G, & LTE for any phone with any carrier for home, office, or car. We’ve boosted over 10,000,000 sq ft of signal for homes, buildings, and vehicles across America and Canada.
- Free consultation (ask us anything) with our US-based customer support. Email: (sales@wilsonamplifiers.com). Phone: 1-800-568-2723.
- Free shipping. Usually ships same day.
- 90-day (seriously) money back guarantee. You want to make sure you’re satisfied.
Our goal is simple: keep people connected. Ask us anything and we’ll be glad to help.
Interested in Learning More? Check Out Our Signal Boosting Info Center
THE WILSON AMPLIFIERS ADVANTAGE
FREE SHIPPING No Minimum Purchase
90-DAY Money Back Guarantee
LIFETIME Technical Support
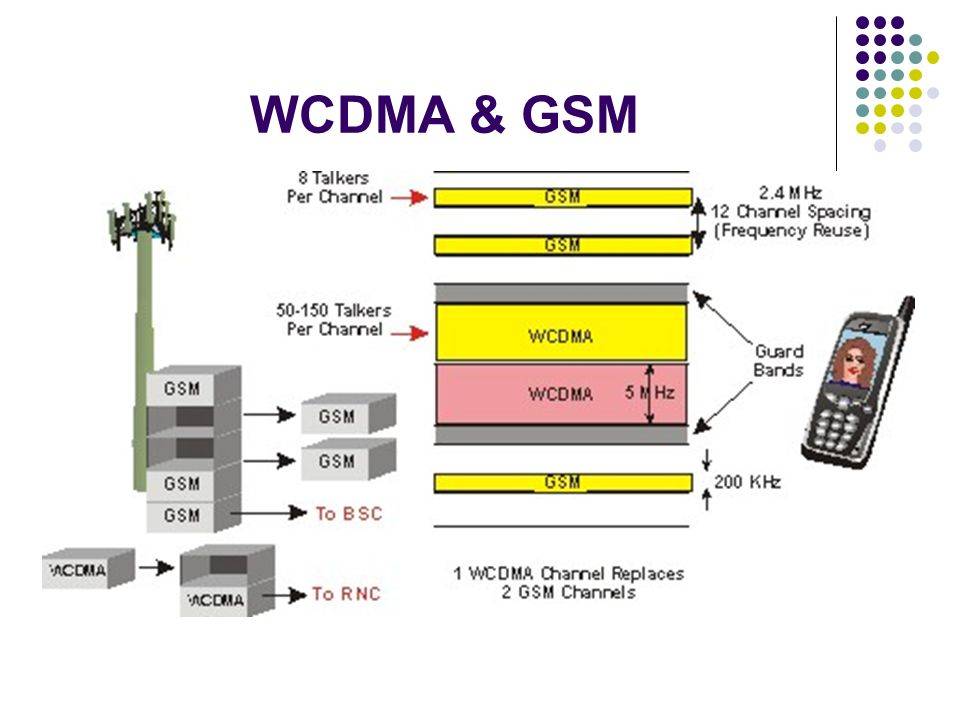
Что такое WCDMA
Сотовая связь WCDMA, которая является аббревиатурой для широкополосного многопользовательского доступа с кодовым делением каналов или широкополосного CDMA, является стандартом мобильного телефона, который объединяет CDMA и GSM для создания совершенно новой системы.
Это один из самых важных атрибутов, когда речь идет о мобильной сети третьего поколения (технология мобильных телефонов 3G). Несмотря на то, что термин WCDMA часто используется взаимозаменяемо с UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications Systems), это технически некорректно, поскольку WCDMA является всего лишь примером UMTS
Международный роуминг с GSM и CDMA
Там, где международные деловые поездки являются проблемой, GSM прыгает вперед в борьбе за звание «Самый доступный». Поскольку GSM используется на более чем 74% рынков по всему миру, пользователи трехдиапазонных или четырехдиапазонных мобильных телефонов могут путешествовать по Европе, Индии и большей части Азии и по-прежнему использовать свои мобильные телефоны. Однако CDMA не обеспечивает многополосную связь, и поэтому вы не можете легко использовать ее в разных странах. Однако некоторые телефоны, такие как iPhone 5, теперь имеют встроенный четырехдиапазонный GSM, поэтому их можно использовать за рубежом со специальными тарифными планами от операторов.
Understanding Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)
GSM is a digital cellular technology that provides mobile data and voice services across devices. Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is one of the second-generation telecommunication standards (2G). GSM simply is a wireless network for transmitting data across mobile devices. It has been misunderstood as a mobile phone in some countries and still is even today. However, GSM is not a mobile phone but a means of communication across digital cellular devices.
The benefits of GSM include a secure network, extensive coverage, and compatibility with a broad range of accessories and handsets. On the other hand, one of the most significant disadvantages of the GSM is that many users share the same bandwidth. This may result in bandwidth limitations and interference.
GSM-world reports that there are two billion GSM mobile phone customers globally. China, Russia, India, and Germany are the most significant GSM users in the world. Since many GSM network customers have roaming agreements with international operators, consumers often use their smartphones while traveling abroad.
See More: How Ericsson Is Fixing IoT Implementation Challenges for Businesses: Q&A With Kyle Okamoto